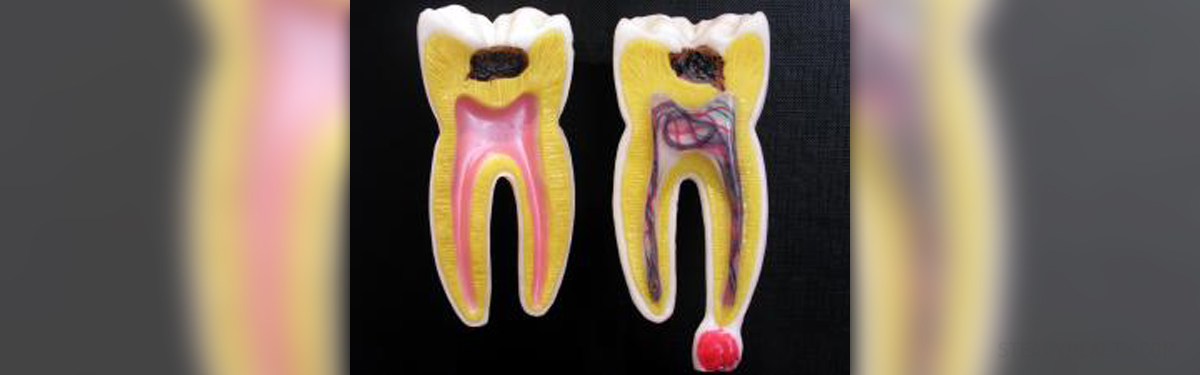
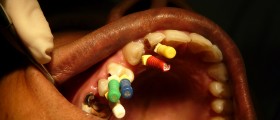
A tooth abscess also known as root abscess is a collection of pus that results from bacterial infection. The infection starts with the soft pulp of the tooth and becomes more severe finally leading to pus formation and may potentially spread to nearby tissues such as gums or jaw bones.
The abscess usually develops in case of dead pulp tissue and in patients with untreated tooth decay, those with cracked teeth or people suffering from extensive periodontal disease. Furthermore, a failed root canal treatment may be another cause of tooth abscess.
Tooth abscesses can be classified into a gingival abscess, a periapical abscess and a periodontal abscess. In a gingival abscess the infection affects only the gum tissue and there is no affection of the tooth or the periodontal ligament. In a periapical abscess the pus accumulation starts within the dental pulp and in a periodontal abscess the condition starts in the supporting bone and tissue structures of the teeth.
Clinical Characteristics of Tooth Abscess
Tooth abscess commonly features with pain that is intensive and is usually described as gnawing, sharp, shooting or throbbing. The pain can extremely intensify if one puts warm compress on the affected area. Furthermore, tooth abscess leads to swelling of the gum around the affected tooth and there may also be swelling of other surrounding tissues. Swelling and pain can be alleviated with cold compresses.
In severe case of tooth abscess there is a chance of bone perforation and this leads to pus draining into the surrounding tissues and the swelling may become even more intensive. The pus can also drain into the oral cavity and cause bad breath. In some patients regional lymph nodes (neck lymph nodes) enlarge as a response to infection.
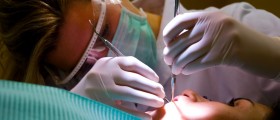
Treatment for Tooth Abscess
The goal of the treatment is to save the tooth (if possible) and clean the affected area form the pus. Still, in many cases the infected tooth is extracted and this procedure can be accompanied by curettage of all apical soft tissue.
The treatment may not be successful and there are several potential complications such as cyst formation, inadequate root canal therapy, vertical root fractures, foreign material in the lesion and associated periodontal disease. In case of abscess of the upper teeth there is a chance of penetration into the maxillary sinus. This is one serious complication that carries life-time consequences.
If left untreated tooth abscess may cause spread of the infection onto the nearby bone and soft tissues. This increases chance of osteomyelitis and cellulitis. One more complication of untreated tooth abscess is formation of fistula, an irregular communication between the affected tooth and surrounding structures.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...