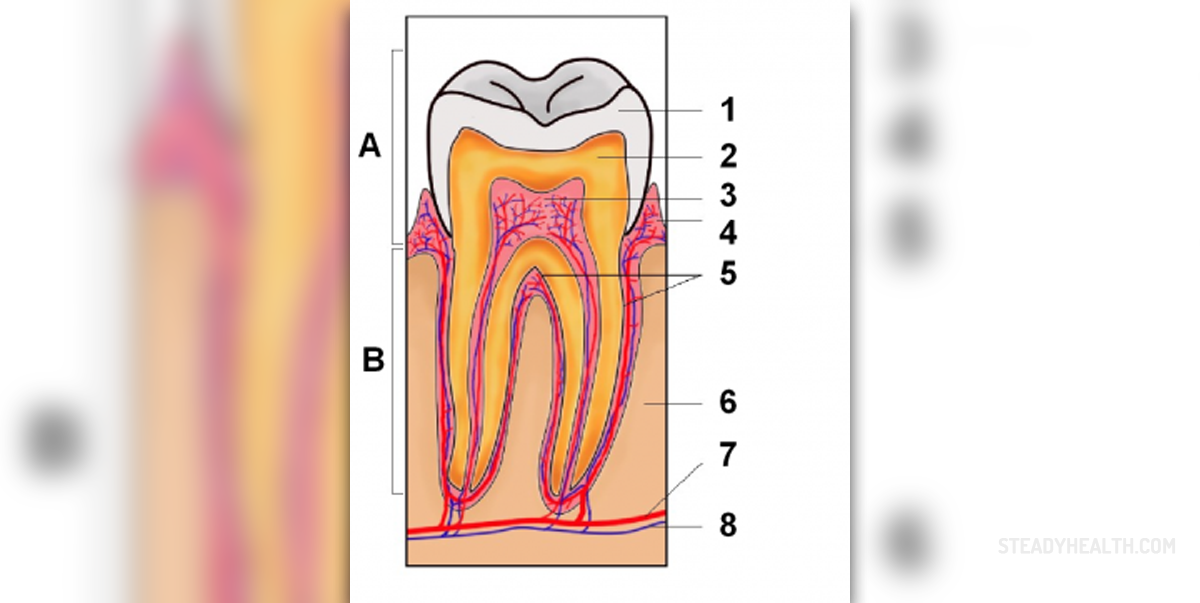
Tooth infection, also known as a tooth abscess, is considered rather painful dental problem and the entire process is caused by bacteria that are normally found inside the oral cavity. Still certain predisposing factors allow these bacteria to affect the tooth and cause the infection. This particularly refers to poor oral hygiene, dental cavity or gum disease. The infection affects dental pulp, gums around the tooth and may spread to the nearby bones.
Tooth infection typically features with general discomfort, severe toothache, and pain during chewing, bad breath, increased sensitivity of the affected tooth to cold and hot. The person may develop fever and in severe form of the infection there is swelling of the underlying jaw.
Causes of Tooth Infection
Certain factors and illnesses are potential triggers for tooth infection. They include dry mouth, gum disease, weak tooth enamel, cracks in tooth, dental cavity and tooth decay. Some of the previously mentioned are associated with poor oral hygiene and some result from inadequate diet.
The oral cavity normally contains different bacteria. They are necessary for certain processes but if the food we eat remains between the teeth or around them and the food particles are not cleaned properly; they represent an excellent source of excessive multiplication of oral bacteria. Furthermore, bacterial multiplication is increased in case there is plaque. Once the bacteria have damaged superficial structures of the tooth they enter deeper layers, affect the dental pulp and spread to the underlying tissues.
Symptoms of Tooth Infection
The most prominent symptom of tooth infection is mild to severe toothache. The pain is either acute or chronic and in majority of patients it is continuous. Other people complain about throbbing or sharp pain. Toothache intensifies during chewing. The presence of infection is responsible for gum soreness and bad breath. Accumulation of puss leads to swelling of the jaw and some people also develop fever and fatigue. The infected tooth is highly sensitive to cold or hot foods and drinks. Apart from accumulating inside the affected tooth the pus also collects in the tissues which surround the affected tooth. The body reacts to infection with enlargement of the regional lymph nodes.
Treatment for Tooth Infection
The treatment options for tooth infection include antibiotics, root canal treatment and tooth extraction. Antibiotics are necessary to kill the bacteria responsible for infection. Root canal treatment is a procedure in which a dentist drills out the root canal and infected area, cleanses the infection and after the infection is brought under control the dentist reseals the tooth. And finally, the last option is tooth extraction, cleansing of the infected area and allowing the wound to heal.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...