The ovaries are located in the pelvis of a woman and are approximately the size of an almond, they are a huge part of the reproductive system. They are what make the hormones for a woman called estrogen and progesterone their job is also to let out the eggs to the fallopian tube down into the uterus also known as the womb. The levels of hormones produced are significantly reduced and the eggs discontinue to be released when a women goes through her menopause.
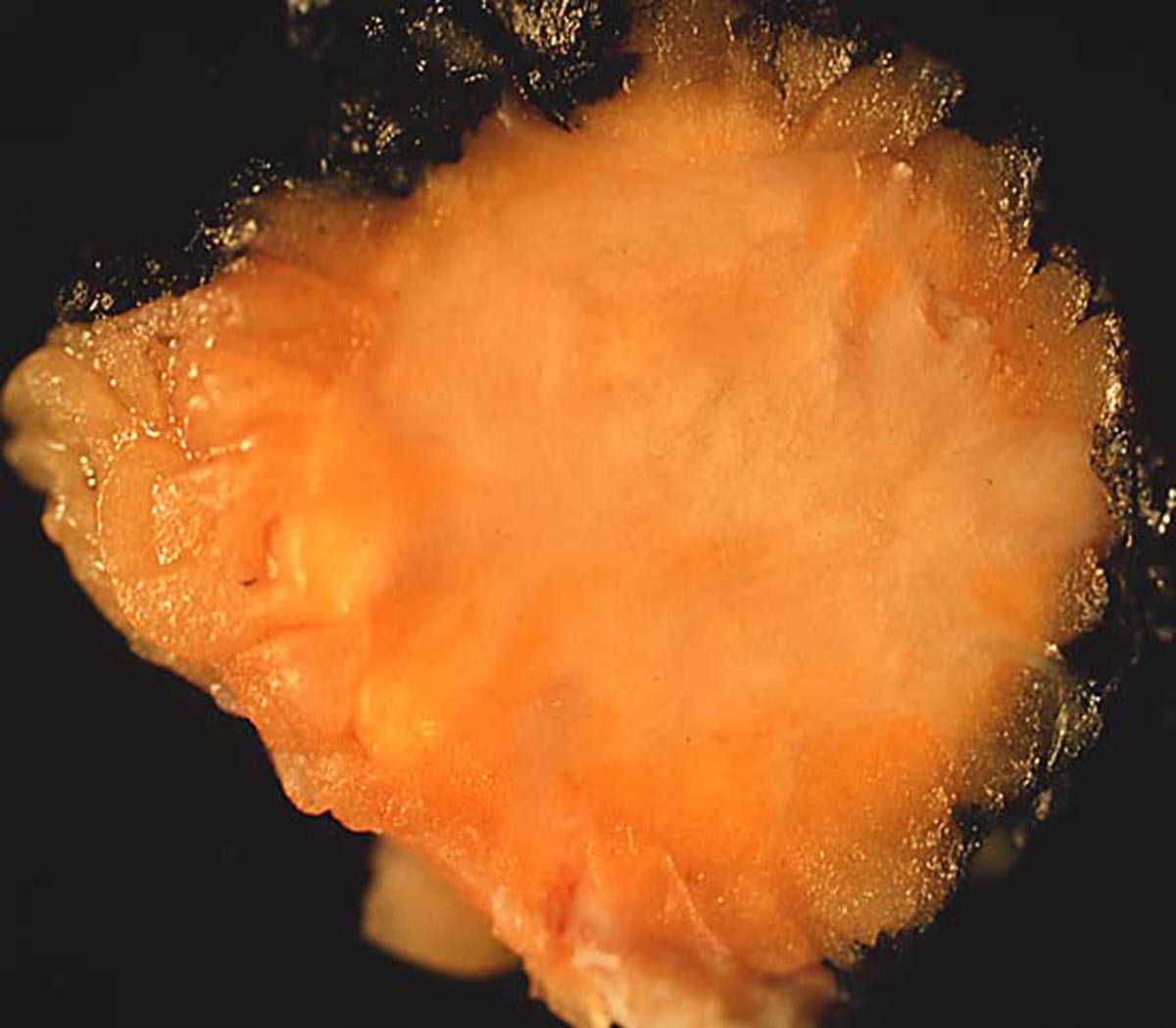
The body contains organs, the organs are made of tissue which is made from cells and this is where cancer can start to originate from. The usual process for cells is to develop, divide, die and replace. However what sometimes can happen is brand new cells start to develop even when the other cells have not died or vice versa the older cells decide not to die in the time in which they are scheduled to die. So what happens is the new cells have nowhere to go, so they form a mass called a tumor or a growth. Some of these tumors are not necessarily malignant which in medical terms means they are benign and a more often than not a threat to your life and can most of the time be removed without ever growing back. These benign cells do not spread or invade other tissues around the body. Malignant tumors are a different story they can threaten your life and they are more serious. As with the benign tumors malignant tumors can be taken off but they do have a tendency to come back and unlike the benign tumor malignant tumors can and will invade and take over other tissues in the body by breaking off the original or primary tumor and going through the lymphatic system or bloodstream this is named metastasis.
The majority of cysts in the ovaries are actually benign, they usually contain fluid, sometimes tissue will be found either on the surface or inside the ovary. More often than not the cyst will dissipate over time if it does not then the doctor will probably do some tests to ensure it’s not cancerous. A rare but significant ovarian cancer can go to other organs situate next to the ovaries and if it invades the bloodstream then it can attach just about anywhere.
Always understand your body and take the necessary steps if you feel things are not right like shortness of breath, sickness and abdominal pain are just a few to mention.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...