Difficulties with esophageal cancer
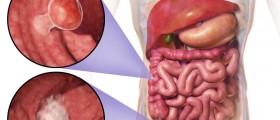
Cancer starts in the cells, from which the tissues are made of. All the organs of the body consist of tissues. The normal process of cells is growth and then division in order for the new cells to be formed. The body has constant need for cells and that is why new ones are formed all the time. Once the cells become old or damaged, there are new ones to replace them. However, the process does not always go this way and in some situations the new cells are made when there is no need for them and the old or damaged ones do not die. When there are too much cells, they form a mass of tissues known as growth or tumor. The tumors are not always cancerous or malignant, they can also be benign or non cancerous. Unlike malignant tumors, benign ones do not often threaten life, can be removed without growing back again, do not attack the surrounding tissues and do not spread to other body parts. On the other hand, malignant growths are more often a threat to life, can grow back after being removed, can invade the surrounding tissues and organs and usually spread to other parts of the body.The inner layer of the esophagus is the place where cancer cells are first seen in almost all patients diagnosed with esophageal cancer. From the inner layer the cancer goes deeper into the esophagus and the tissues that surround it. By breaking away from the original tumor the cancer cells spread. The most usually seen way of spreading is through blood vessels and lymph nodes, as these branch into every tissue. When cancer cells attach to some other tissue, they may develop new tumors that will cause damage to that tissue. The process of spreading of cancer cells is known as metastasis.
Four stages of esophageal cancer exist and the fourth stage is the final one. In the first stage the cancer has grown through the inner layer of the submucosa, while in the last stage the cells have invaded distant organs, like the liver, for instance.Metastasis of esophageal cancer
A patient who is diagnosed with stage IV of esophageal cancer is considered to have metastatic cancer. That means that the cancer is not only located in the esophagus any more but has spread to other organs, which are not near the esophagus. The situation for patients diagnosed with stage IV esophageal cancer is not the same as that of patients diagnosed with the cancer in the early stages. The circumstances that are seen in stage IV are not seen anywhere else and they will have great influence on the treatment, along with the prognosis factors.The usual ways of treatment are not often used if the patient is in the final stage of esophageal cancer, as the prognosis is not good and they are mainly used to provide relief. Clinical trials are mainly referred treatment option in this situation. Clinical trials study the effectiveness of new drugs or treatment strategies. However, these new ways of treatment cannot be tested if the patients do not apply for the clinical trial.
A patient who takes part in a clinical trial will have access to better treatments and will play a vital part in learning more about the ways of treating cancer. However, before participating in the trials, the patient needs to talk to the doctor and get to know all the possible risks and benefits that that trial may provide.The best possible treatment for the final stage of esophageal cancer does not consist of only one therapeutic approach. In almost all situations when treatment of stage IV esophageal cancer is considered, a whole team of specialists will be included in the process of treatment. The team usually includes an oncologist, radiation oncologist, surgeon, nutritionist and gastroenterologist.
The standard curative therapy for the final stage of esophageal cancer does not exist at the moment. The current treatment provides short-term benefit and focus on the improvement of nutrient intake. The goal of the treatments that are used at the moment is to prolong survival and lessen the effects of the symptoms. Palliative surgery is only one of the possible treatment options for this stage of cancer of the esophagus. However, this surgery does not cure the disease but only provides the relief for the symptoms. Other treatment modalities like laser ablation, photodynamic treatment and esophageal dilation, among others are used.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...