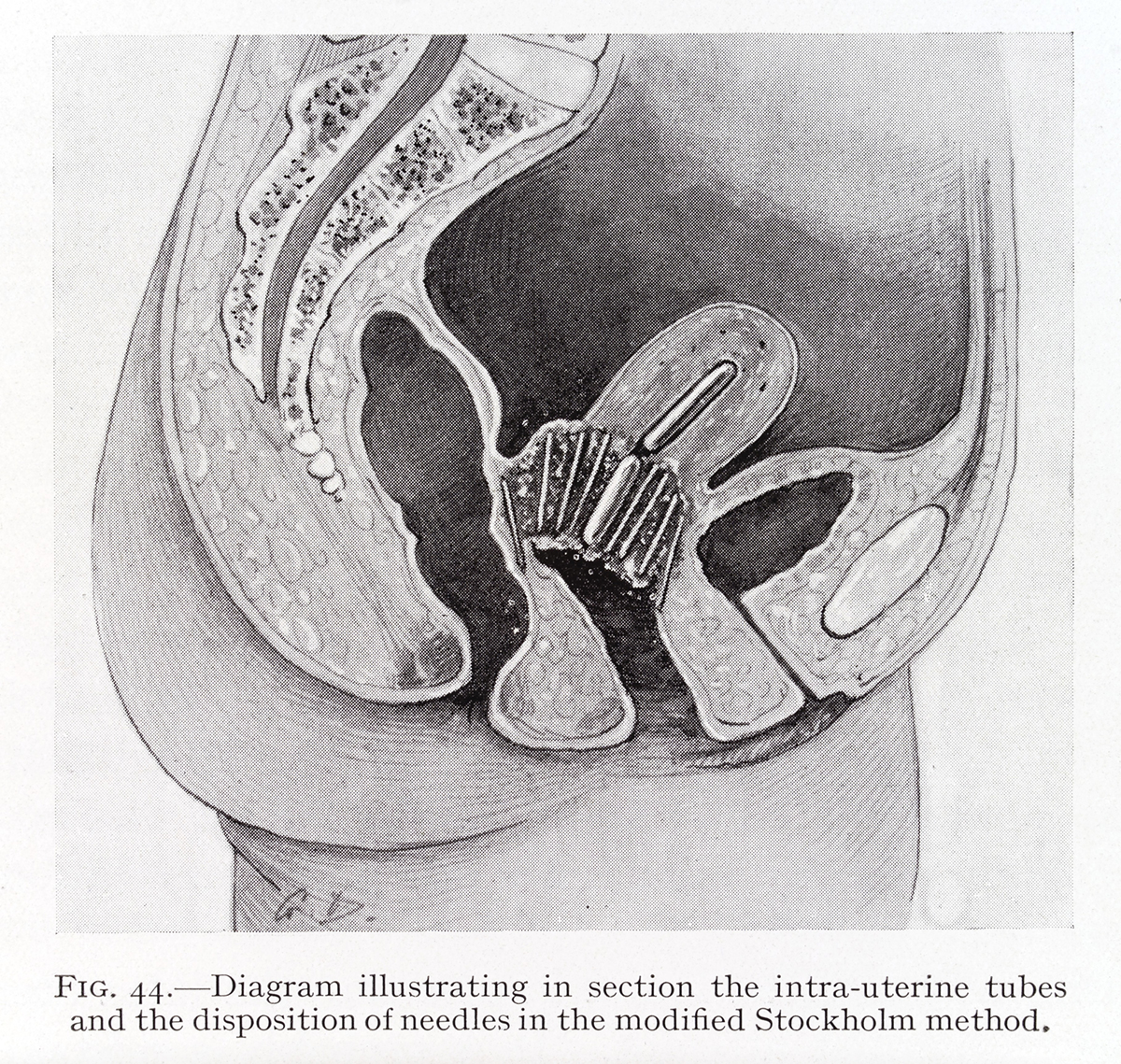
Cervix is a part of uterus, female reproductive organ that is located in pelvis. The cervix is connected to vagina, so the blood during the menstrual cycle runs from the uterus through the vagina. The function of the cervix is to produce special mucus. This helps fertilization. When a woman is pregnant the cervix is very tight preventing the baby to come out while at childbirth it opens enough to allow baby to come out.
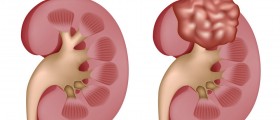
Cervical cancer is a malignant disease starting its development from cervical cells. Cells are the smallest components of tissues which are the parts of organs and system of organs. Normally cell grow and divide up to a limit in order to replace the old ones or or the once that died. But sometimes the process goes out of control where cells multiply without limit and then a tumor occurs. Cervical tumor can be both benign and malign. Unlike benign malignant tumors are serious and can even lead to death.Cervical cancer starts its development within cervix and then spreads to surrounding tissue and pelvic or far away organs (metastases).
Early stage of the disease is usually without any symptoms. In this stage the cancer can be diagnose by simple test (Pap smear or cervical smear test) if a woman visits her gynecologist on regular bases (at least once in a year). In advanced stages abdominal vaginal bleeding can occur. The bleeding between menstrual period is also a possible sign of cancer. Bleeding during and after sexual intercourse or pelvic examination, bleeding after menopause period or prolonged menstrual periods which extensive than usual. Symptoms include pelvic pain, pain during intercourse and even heavy vaginal discharge. If any of the previously mentioned symptoms occur the patient should visit gynecologist as soon as possible.
To reduce the risk of getting cervical cancer or to increase chances of establishing the diagnosis at an early stage it is recommendable for patients to have regular Pap tests. This simple test can even point to some abnormalities which can lead to cancer. These abnormalities are curable and if they are found on time and treated properly the cancer does not develop. The very test is conducted during gynecologist\'s pelvic examination when he or she scrapes samples of cells from the cervix. These samples are then checked microscopically. If the test is abnormal further investigation is recommended. The patient need to have both colposcopy and biopsy done. The sample taken by biopsy (punch biopsy, LEEP method, encocervical curettage) is further analyzed for malignant cells. As for cone biopsy this one helps establishing whether the cancer spread in the tissue beneath the surface of the cervix. There are no complications after biopsy only minor pain when painkillers are suggested.



_f_280x120.jpg)







Your thoughts on this
Loading...