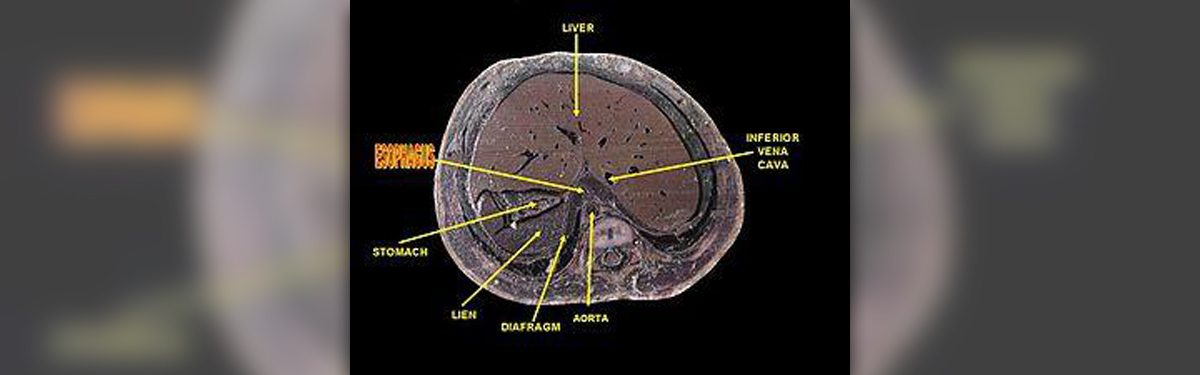
The esophagus is an organ of the gastrointestinal tract. It is located in the chest and is approximately 10 inches long. The food we consume is initially chewed in the oral cavity and then is, with the assistance of the tongue, transferred into the esophagus and from there it reaches the stomach.
Similarly to other digestive organs, the esophagus is a multi-layered organ. The inner layer or mucosa is moist and is made of specific cells which may transform into malignant ones. The second layer is submucosa. It contains many glands which produce mucus necessary for the moist of the inside of the organ. The third layer is muscle layer. As the name suggests this layer contains muscles. The function of esophageal muscles is to push the food into the stomach. Finally, the outer layer of the esophagus covers the organ and is anatomically known as adventitia.
Tumors of The Esophagus
Under normal circumstance, cells of each and every organ grow and divide when they are supposed to. So, healthy cells replace the old ones. However, this process sometimes gets out of control and some cells may transform and start multiplying uncontrollably. After some time these cells form tumor growths and are blamed for many symptoms and signs.
Esophageal tumors are classified as benign and malign. Benign esophageal growths do not pose a treat, can be easily removed and never invade the surrounding tissue of the esophagus or the nearby organs. Finally, these tumors do not give metastases i.e. never spread to distant organs. Malignant esophageal growths, on the other hand, are serious tumors. They can be surgically removed but there is also chance of cancer recurrence. These tumors invade the surrounding esophageal tissues and nearby organs. Malignant esophageal tumors are also capable of entering the blood and the lymphatic system from where easily spread to distant organs in the body.
Diagnosing Esophageal Cancer
People who have been having certain problems which are most definitely associated with malfunctioning of the esophagus such as dysphagia (difficulty swallowing), odynophagia (painful swallowing), or feel chest pain, pressure or burning as well as fatigue, indigestion, coughing and hoarseness may be affected by esophageal cancer.
In order to confirm or rule out esophageal cancer, doctors need to perform physical exam as well as several other tests and exams.
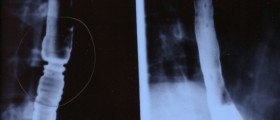
Apart from blood test, one firstly undergoes barium swallow. This procedure includes drinking a barium solution while at the same time the doctor takes X-ray of the esophageal area. The presence of barium allows better visualization of the esophagus and the tumor. After barium swallow, one undergoes endoscopy. During endoscopy the doctor inserts a thin, lighted tube and inspects the inside of the organ. While performing endoscopy(esophagoscopy) doctor may take samples of suspicious tissue. Samples obtained by biopsy are sent for pathohistological examination. This is the final test which confirms or rules out the cancer and also gives more information regarding histological type of the tumor.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...