Ovarian Cysts
Nowadays, one of the most frequent conditions affecting almost every woman is ovarian cysts. Women who are of childbearing age are at high risk to develop this condition. Many women become very frightened when they discover that they have this condition.
Ovarian cysts are benign growths within the ovaries or on the surface of one or both ovaries. In the majority of cases, ovarian cysts are not serious health conditions. They merely cause any discomfort. However, when they grow large, they can cause uncomfortable pain in the lower abdomen or pelvis region.
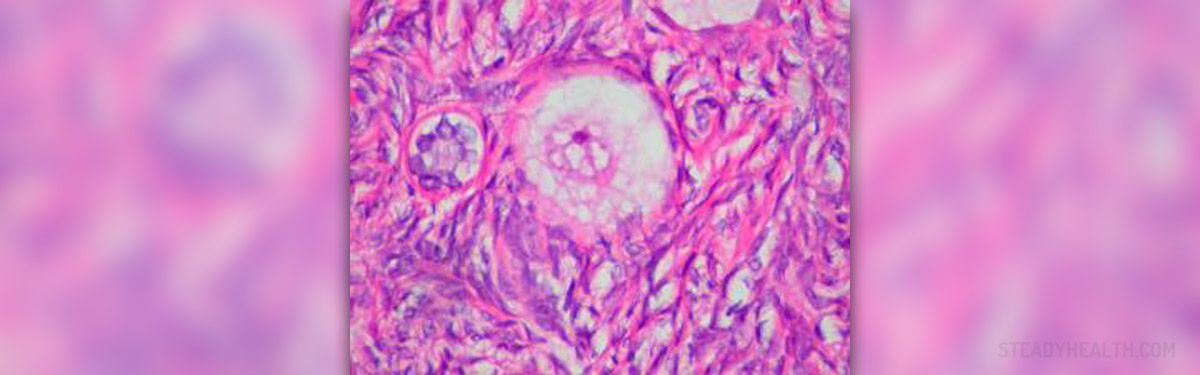
In most cases, the ovarian cysts do not require medical attention and gradually disappear on their own, there are cases when the ovarian cysts become serious and even lead to the developing of many serious health problems, such as cancer.
Ovarian Cysts and Ovarian Cancer
When the cancers are in question, every twentieth is ovarian cancer. It is thought that the cause of ovarian cancer is the ovarian cyst. The ovarian cysts can also cause colon cancer, as well as the uterus cancer. When the ovarian cysts start to grow very fast and expand to the tissues of the surrounding organs, tumors are formed. One should know that tumors can be benign and malignant.
Benign tumors are not serious health conditions. On the other hand, malignant or cancerous tumors are very dangerous because they cause cancer, which is a very fast progressive disease that destroys healthy body cells.
Ovarian cancers may be divided into several types, but the most frequent is the epithelial ovarian cancer developed out of the cells that are on the surface of the ovaries. Germ cell ovarian cancer is another type of ovarian cancer developed out of the cells that are within the ovaries. Other two rare types of ovarian cancer are the stromal ovarian cancer and primary peritoneal cancer.
Colon Cancer and Ovarian Cyst
Several studies proved that colon cancer could be caused by ovarian cysts. When the ovarian cysts cause ovarian cancer, it can spread to the tissues of the uterus, as well as to the colon, thus forming uterus and colon cancer.
Furthermore, many other organs may be affected and the cancer can even expand to the lungs. Therefore, it is very important to regularly control the ovarian cysts in order to prevent these serious complications that can arise from untreated ovarian cysts.
- Ovarian cysts are typically asymptomatic and often discovered incidentally, but may present with pelvic pain and/or menstrual changes. Most can be treated symptomatically with pain control and monitored for progression. However, if large enough, they may cause obstructive symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, distention and early satiety. Due to the rare incidence of giant ovarian cysts, the clinician may be unlikely to consider them as a diagnosis when evaluating a patient with these symptoms.
- Due to the widespread use of modern imaging techniques such as ultrasound and CT, the incidence of giant ovarian tumors is exceedingly rare in industrialized nations. Documented giant ovarian cysts also tend to be reported from developing countries rather than industrialized nations. This likely reflects the decreased access to modern healthcare found in these countries.
- If discovered incidentally on CT, labs should be drawn for a CA-125 level. A mass under 5 cm and a normal CA-125 (
- Due to the rarity of giant ovarian cysts, their surgical management has not been well studied with randomized trials. However, giant symptomatic cysts, or complex ovarian tumors over five centimeters or patient with a rising CA-125 should have surgery. Traditionally, all giant cysts were treated with laparotomy, but laparoscopy has become popular and may be appropriate in certain cases, especially uncomplicated smaller cysts. Laparoscopy may be appropriate for patients with a very low risk of malignancy, and has been well documented in premenopausal patients.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...