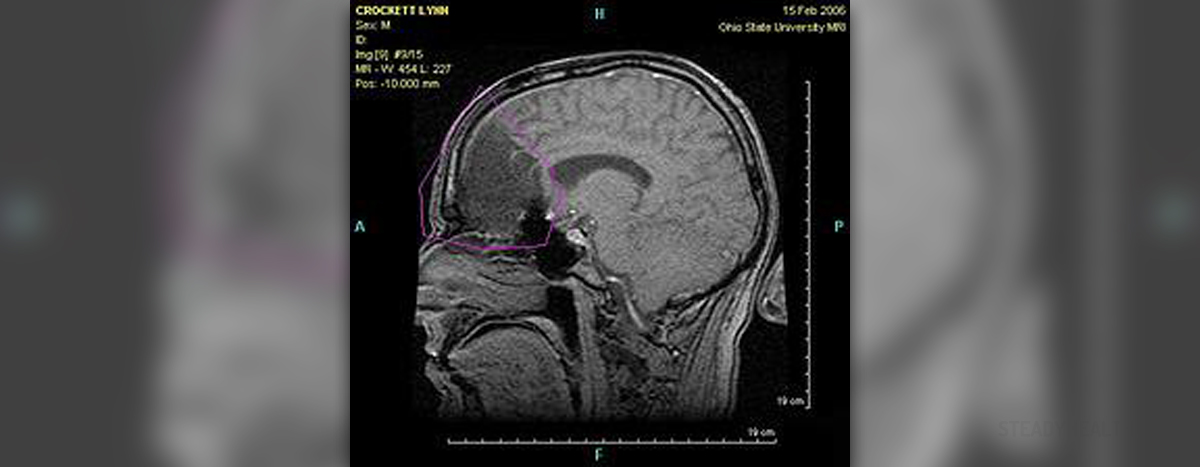
The brain is a mighty organ controlling all the functions in the body allowing all the organs to act according to the body's needs. Any damage to the brain's structure results in changes in functions the affected portion is in charge of. One of the illnesses that typically cause damage to various structures of the brain and brain cells are brain tumors. These neoplasms may be benign or malignant. Once they form they tend to grow, expand, irritate, compress or even destroy nearby cells which eventually precipitate various problems. So, each and every brain tumor must be taken seriously and treated adequately.
Brain Tumors
Brain tumors may form anywhere in the brain and affect various parts of the brain. Since the organ is anatomically divided into three major parts, the cerebrum, cerebellum and brain stem, and all of them are in charge of different functions it is clear that tumor affecting one of these parts will have distinctive characteristics compared to brain tumors originating from other two portions of the brain. The cerebrum is practically the largest parts of the brain. It has various function. The cerebrum, for instance, controls reading, learning, speech and emotions. This part of the brain is further divided into two hemispheres, the left and the right each controlling the opposite side of the body. So, if one has a brain tumor in the cerebrum, he/she might experience cognitive and memory issues among other problems and there may be loss of control over the opposite side of the body compared to the affected hemisphere of the cerebrum. The second part of the brain, the cerebellum controls functions such as balance, walking and taking. So, if the cerebellum is affected by a brain tumor, one may easily experience problems regarding balance and speech. Finally, the brain stem is the structure located bellow the cerebellum. It comprises two vital centers, the one controlling the blood pressure and the other controlling breathing. Tumors in this region may easily cause abnormalities in heart action and can precipitate breathing issues. The brain stem also controls hunger and thirst, body temperature and the mentioned function may be affected as well once the tumor forms.
All brain tumors are easily classified into benign and malignant. Now, benign tumors can be surgically removed, they rarely grow back and cause any serious problems. However their location may make them inoperable, they might grow rapidly or sometimes transform into malignant tumors, all of which are not good prognostic signs. Malignant tumors, on the other hand, are always harmful, grow rapidly, spread through the entire brain, may give metastases and cause lethal outcome in relatively short period of time. Malignant tumors of the brain can be additional divided into primary and secondary where primary brain tumors originate from the cells of the brain while secondary actually represent metastases of a tumor that initially affects other organs in the body.
Brain Surgery as a Treatment Option
There are several treatment options patients suffering from brain tumors may undergo. These include surgery, radiation therapy and chemotherapy. Even a combination of treatments is possible. Supportive care and palliative treatment are indicated in later stages of the disease.
When it comes to brain tumors most doctors first opt for surgery. It is best if the tumor is removed completely. Sometimes the tumor is partially resected while the rest of it is treated additionally. The problem regarding brain tumors is many times their localization and the relation to nearby structures. For instance, the tumor may be benign but situated deep in the brain or in parts that simply must not be manipulated because it is highly likely that the person will die or end with permanent neurological sequalae. Tumors located in the brain stem are inoperable. Also, surgery is not an option for elderly people and those with a variety of comorbidities. So, even though surgery can cure benign tumors of the brain, it may not be performed because of other reasons.
Patients in whom the tumor is not completely removed, inoperable patients and those in whom the tumor have been removed but it is malignant in nature require additional treatment. They most commonly undergo radiation therapy.
Today, thanks to many medical advancements surgeons may perfectly locate the site of the tumor and plan the surgery in such a way to be highly successful and minimally destructive to nearby healthy tissues. Also, there are approaches that practically do not involve removing the scalp. This refers to gamma knife (radiosurgery), which is actually a medical procedure used to target lesions in the brain and remove them efficiently. Radiosurgery involves direct focusing of beams of ionizing radiation with high and almost impeccable precision. Gamma knife is used instead of open surgery for small brain tumors and those that cannot be reached in other way. The radiation affects only the tumor and spares all the surrounding tissues (arteries, nerves and other vital structures). Also, this approach may efficiently deal with certain blood vessels malformations.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...