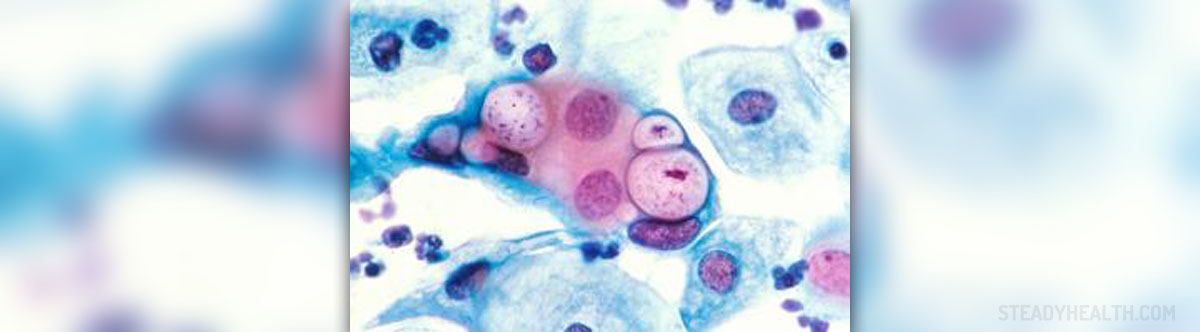
Pap Smear Test
The Pap test (or the Pap smear) is a test used to detect the changes of the cervix cells. If the cervix cells have changed it may indicate the precancerous condition or cervical cancer. Both conditions can be treated and completely cured if caught in early stages.
The Pap test is done during the pelvis exam at the gynecologist. He/she will use a speculum to examine the vagina and with a small brush collect the cervix cells. The procedure itself is a bit uncomfortable sometimes, but it’s not painful. The cells are then transferred to the solution and sent to the laboratory to be tested.
Results of the Pap test
It takes several weeks for the lab results to be done (usually 2 to 3 weeks). Pap smear results can be normal or abnormal. If they are normal, it means that there are no changes whatsoever in the morphology of the cervix cells.
Abnormal Pap smear indicates some changes of the cervix cells (not always the cancerous changes). Your gynecologist may decide to take another Pap test and/or some additional tests, such as colposcopy or STD (sexually transmitted disease) tests. Repeated test is necessary if there was an infection at the time of the test, or there weren’t enough cells to perform the testing. Women in menopause might also need to repeat the test. In some cases, they will need to take estrogen medications, to avoid the influences to the Pap smear.
Abnormal result may require colposcopy, which is a special microscope, used to examine vagina and cervix. Gynecologist will use speculum to widen the vagina and use a colposcope to see the potential problem. This instrument works as a magnifying glass and helps to detect the cervical changes closely. You shouldn’t worry about the instrument, since it is not inserted in the vagina during the exam. Sometimes, your doctor will need to take some tissue sample, to perform the biopsy of the abnormal cells.
To provide accurate Pap test results, it is necessary to avoid sex, vaginal creams and douching for 48 hours before the test.
When to Take Pap Test
Every woman older than 21 years should take the Pap test every two years. If you are 30 or older and had 3 consecutive normal Pap results, the test is recommended once in 3 years.
HIV positive, chemotherapy, organ transplant, chronic steroid and diethylstilbestrol (DES) exposed patients are at risk of developing cervix changes and should be checked more frequently.
Hysterectomy patients with partially removed cervix should still perform routine Pap smears and those with the total hysterectomy are advised to do pelvic exams once a year.
Abnormal bleeding and vaginal discharge should always be reported to your gynecologist, because they might indicate the cancerous changes of the cervix.


_f_280x120.jpg)









Your thoughts on this
Loading...