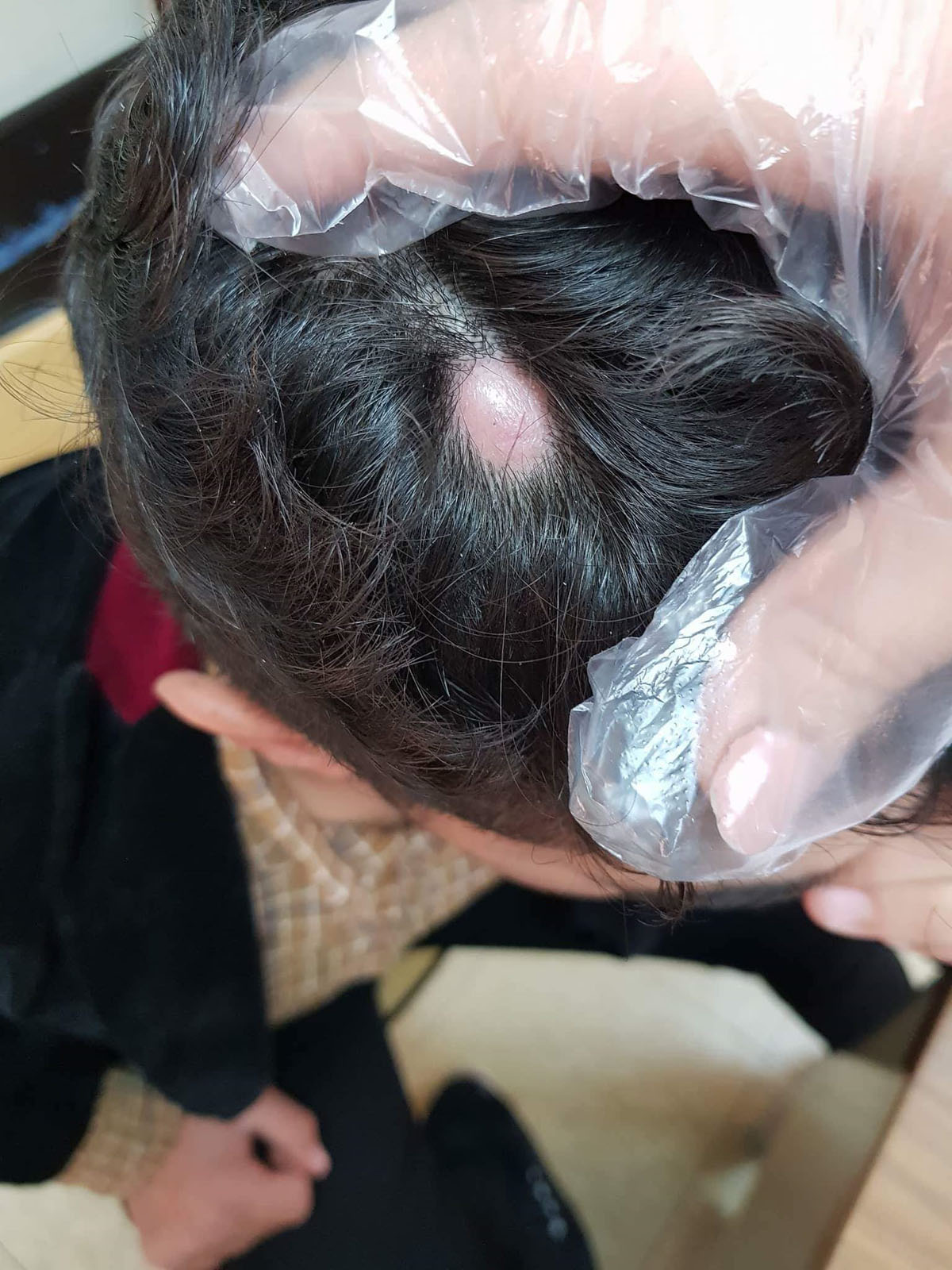
What is a sebaceous cyst?
Sebaceous cysts, also called wens, are formations that develop underneath the skin. They are filled with white, fatty, and semi-solid material, called keratin — the same substance that makes up your hair and nails. These cysts usually appear on the scalp, neck, behind or on the ears, on the back, or on the upper arms. Men can have them on the scrotum as well. Sebaceous cysts can appear anywhere on the body except on the palms of your hands and soles of the feet. They tend to appear on hairy parts of the body, however, and in time they cause hair loss on the part of the skin just above the cyst. Sebaceous cysts are usually round, smooth and can be of different sizes.
Sebaceous cysts can be caused by a blocked sebaceous gland or hair follicles or by overproduction of testosterone.
Generally, these cysts are not considered to be medically dangerous and they usually do not require treatment. However, if they are painful, if they grow or get infected, or simply if they are unsightly, sebaceous cysts can be surgically removed during a simple and routine procedure;
Surgery for sebaceous cysts
Surgery to remove sebaceous cysts is simple and safe and it is performed in order to remove completely the cyst's sac and its contents.
The procedure can be done by wide excision, minimal excision or punch biopsy excision.
This surgery is usually done in a clinic as a outpatient case, which means that there is no need for the patient to stay overnight. In most cases sebaceous cyst removal is carried out with the help of a local anesthetic, injected in the area close to the cyst.
The surgeon opens the lesion with a scalpel, using different types of incisions, depending on the size of the cyst and the part of the body where the cyst is present. He or she then squeezes out the keratin, which is the hard material inside the cyst that is made mostly of sebum and dead skin cells. When the surrounding area is clean of keratin, the surgeon holds the incision open and uses finger or an instrument to pull the cyst out, being careful not to break it. If the cyst is extracted without breaking, there is 100 percent chance it will not come back.
After the cyst is extracted, the incision is sterilized and then stitched or sewn. It usually leaves a tiny scar, which may disappear in time, especially if the patient uses scar cream.
If, however, the cyst breaks while it is being pulled out, or if it is fragmented and cannot be pulled out integrally, the surgeon needs to clean the lesion thoroughly in order to prevent the recurrence of the cyst. This is usually done by curettage or scraping and the fragments may be burned by electro-cauterization. In this case the cyst may or may not come back. The most important factor here is that the entire sac that made up the foundation of the cyst is removed — which is also why simply draining a sebaceous cyst is not an effective method for patients who want to eliminate these cysts permanently.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...