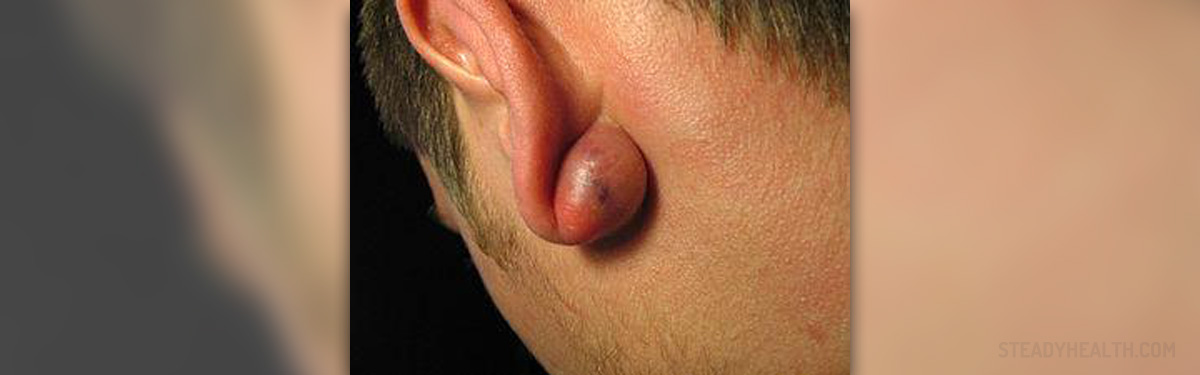
Sebaceous hyperplasia is a skin condition related to the sebaceous glands. This condition is benign and there is no evidence it can progress into a malignant or cancerous disease.
Sebaceous hyperplasia - general info
Sebaceous hyperplasia was once known as senile sebaceous hyperplasia, because it is mainly associated with older age. However, since it can be observed in middle-aged people as well, the term “senile” was dropped. The cases of inherited sebaceous hyperplasia have been reported, in which the lesions appeared much earlier than the middle age. Of the lesions or papules appear in the childhood or adolescence, the condition is then called premature or familial sebaceous hyperplasia.
This condition is characterized by single or multiple lesions or papules on the skin, usually on the areas with increased secretion of sebum, such as the face. Other than the face, these lesions can also appear on the chest, breasts, mouth, penis and vagina. The papules are usually yellow, soft and small.
Causes of sebaceous hyperplasia
With age, the circulation of hormone androgen decreases. This hormone plays an important role in the functioning of the sebaceous glands and their cells, called sebocytes. The sebocytes begin crowding in the gland, causing enlargement or hyperplasia. This usually happens in areas with the highest number of sebaceous glands, such as the face, especially the area around the nose, cheeks and forehead.
Many experts believe that the use of immunosuppressants and exposure to ultraviolet radiation are, along with hormonal changes due to age, the contributing factors for sebaceous hyperplasia.
Treatment for sebaceous hyperplasia
Sebaceous hyperplasia is always benign, which basically means that this condition is more of a cosmetic issue than an actual health concern. However, if they are large or if there is a lot of them, they can cause frustration and annoyance.
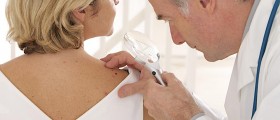
These lesions are relatively easy to diagnose, but most doctors prefer doing a biopsy in order to rule out malignant diseases with similar manifestations, such as basal cell carcinoma.
Lesions can be removed through laser surgery, photodynamic therapy, cryotherapy, which uses liquid nitrogen, cauterization, electrodessication, shave excision and excision. The choice of treatment depends on the patient’s preferences and his or her financial status, since some of them, like the laser, can be expensive. Removal of the lesions may or may not leave scars.
Another course of treatment can involve oral isotretinoin. This therapy can clear some, if not all of the lesions, after two to six weeks, but there is a chance they will come back. This type of therapy is not suitable for everyone and it is available only with prescription.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...