Behçet's disease is a rather rare condition and represents an immune-mediated systemic vasculitis affecting many organs and organ systems in the body. In the majority of cases the condition is characterized by ulcerations on mucous membranes and changes affecting the eyes. The condition is also associated with damage to other organs like organs of the GIT, the lungs, musculoskeletal as well as neurological system.
Behçet's Disease Pathogenesis
Behçet's disease is still a mystery and the actual cause of this medical condition has not been identified yet. What has been confirmed is that the disease in all cases leads to auto-inflammation of blood vessels throughput the body. Many times, diagnosis is set after excluding other medical conditions, but it is also possible to confirm Behçet's disease after pathohistological examination of samples taken from the affected areas.
It is clear that the immune system of individuals suffering from Behçet's disease is overactive and it is blamed for inflammation of blood vessels and subsequent damage to many organs. The reason why the immune system starts acting like this is unknown. This is why there is a need for additional research in order for this condition to be demystified.
Finally, it seems that the condition has something to do with genetics because the first relatives of the affected individuals seem to be affected more compared to people with no family history of the disease.
Behçet's Disease Symptoms and Signs
Symptoms and signs patients have to deal with basically depend on the affected organs/organ systems.
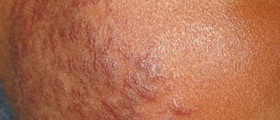
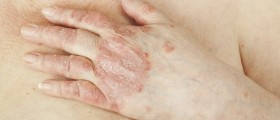
In case the disease affects the skin and mucous membranes, it occurs in a form of painful ulcerations. Lesions in the oral cavity are aphthous-like and non-scarring. Such lesions are recurrent. The one also suffers from painful genital lesions occurring around the anus, vulva or scrotum. These lesions are scarring. Behçet's disease may additionally cause erythema nodosum and cutaneous pustular vasculitis. Finally, some individuals end up with lesions that resemble pyoderma gangrenosum.
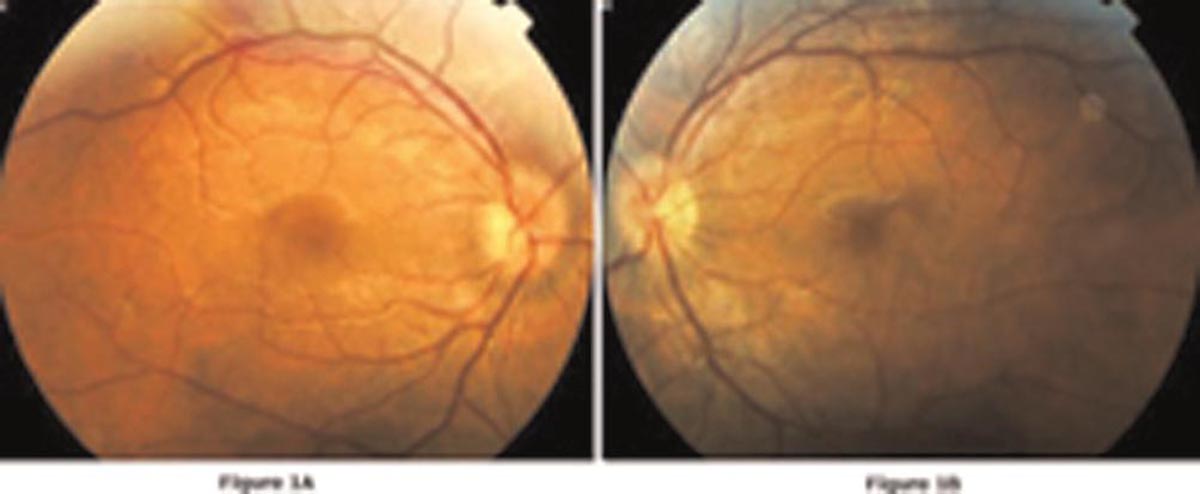
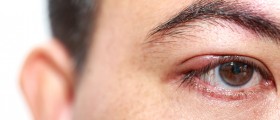
As for the eyes, Behçet's disease is associated with anterior uveitis, posterior uveitis, retinal vasculitis and may in severe cases cause permanent vision loss. Optic nerve involvement is rarely reported even though acute optic neuropathy may occur.
If the condition affects the GIT (gastrointestinal tract), patients complain about nausea and diarrhea (which may be bloody).
In case inflammation is located to the lung blood vessels, patients experience hemoptysis, pleuritis, cough and fever. Aneurysm of the pulmonary artery may rupture and cause life-threatening complications.
Many joints can be affected and such inflammation commonly occurs in a form of non-erosive poly or oligoarthritis. Large joints of the legs are predominantly inflamed.
Finally, Behçet's disease is connected with aseptic meningitis and vascular thrombosis (e.g. dural sinus thrombosis) as well as organic brain syndrome characterized by confusion, seizures and memory impairment. The previously mentioned health issues occur once the disease has progressed. The prognosis in such patients is poor.
Diagnosing Behçet's Disease
The diagnosis of Behçet's disease is established according to clinical criteria and a pathergy test recommended by the International Study Group.Namely, according to this group patients who may be suffering from Behçet's disease must have oral ulcers (aphthous-like lesions of any shape, size and number which occur at least 3 times within a year). Together with the mentioned patients must have 2 out of the following: genital ulcers, skin lesions, eye inflammation and pathergy reaction. Genital ulcers are supposed to affect the genital and anal area and cause swelling of the testes and epididymis in men. Skin lesions may be in a form of papulo-pustules, folliculitis, erythema nodosum and acne. Eye inflammation may occur as iritis, uveitis, retinal vascultiis or the presence of cells in the vitreous. Finally, pathergy reaction is a skin reaction that develops as a result of needle-prick. At the site of testing, patients are supposed to develop papules larger than 2 mm in diameter within 24-48 hours.
Many doctors also take into consideration clinical findings when confirming Behçet's disease. They pay close attention to the presence or absence of mouth ulcers, arthritis/arthralgia, nervous system symptoms, inflammation of the GIT, deep vein thrombosis/superficial thrombophlebitis, epididymitis, inflammation of the cardiovascular system and lungs, problems with hearing and balance, extreme fatigue, changes in personality and psychoses. A family history of Behçet's disease is also of major importance when confirming the condition.
Behçet's Disease Relevant Data
Behçet's disease is rarely reported in the United States. Around 15,000-20,000 people in the US have been confirmed to suffer from Behçet's disease. On the other hand, the condition is more frequent in the Middle East and Asia. This drives to conclusion that it may be associated with tropical climate and may occur as endemic disease. There is no connection between Behçet's disease and cancers of any kind. One study, however, pointed to food allergies (particularly allergy to dairy products) as possible culprits of the disease.
Men are in general more affected than women. It is also confirmed that the condition starts with ocular manifestations which tend to occur at the age of 30. Many ocular manifestations may affect each and every patient and these should never be neglected and taken easily.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...