Crohn’s Disease IntroductionCrohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory disease that affects intestines, bowel and other organs of the digestive system such as mouth, stomach and anus. This illness is characterized by inflammation and ulceration of the affected organs. Both Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis are types of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). Crohn’s disease can develop in people of all age groups although it is most commonly seen in people aged between 15 and 40. It equally affects men and women.
Different changes may occur in the bowel tissue due to Crohn’s disease. Inflammation and ulceration can cause the bowel to swell, thicken and develop scar tissue which can eventually result in obstruction in the organ. The ulcers may penetrate deep into the bowel wall. Crohn’s disease interferes with the ability of the bowel to absorb nutrients from food and may lead to malabsorption. Deep ulcers can create tunnels known as fistulas between different parts of the bowel or between the bowel and nearby organs such as bladder, vagina, skin or anus.
Types of Crohn’s Disease
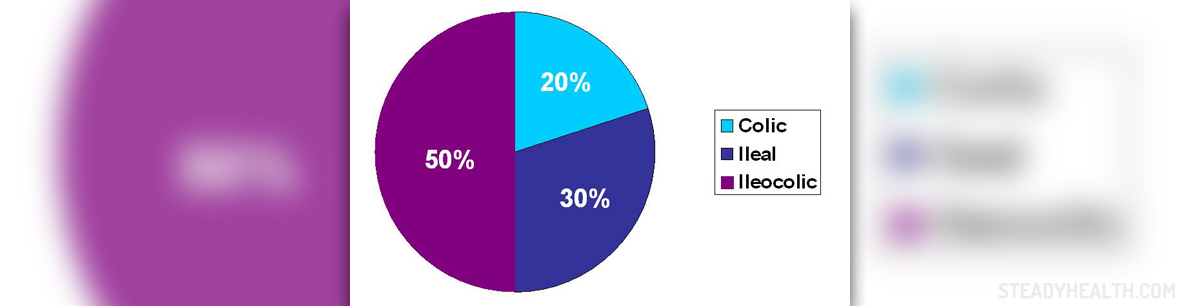
There are five different types of Crohn’s disease that differ by symptoms and area where the disease develops.
Ileocolitis is the most common type of Crohn’s disease. The inflammation and ulceration occur in the ileum (the lowest segment of the small intestine) and the colon. It is accompanied with significant lose of weight, diarrhea, cramping or pain in the middle or lower right quadrant of the abdomen, malabsorption and potentially anemia.
Ileitis is a type of disease that affects the ileum. It causes the same symptoms as ileocolitis but there may be also formation of fistulas in the lower right part of the abdomen.
Gastroduodenal Crohn’s disease is a type of the disease that involves the first segment of the small intestine (duodenum) and the stomach. The symptoms include nausea, loss of weight, loss of appetite and pain in the upper middle part of the abdomen. If there is an obstruction in the bowel, vomiting may also occur.
Crohn’s colitis is a type that affects only the colon and may cause skin lesions, pain in the joints, diarrhea, bleeding from the rectum as well as development of ulcers, fistulas and abscesses in the anal area.
Jejunoelitis is a disease that involves the jejunum or the second and the longest segment of the small intestine. It causes cramping and abdominal pain, especially after meals. Diarrhea and malabsorption that can lead to malnutrition.
Causes of Crohn’s DiseaseScientists have not yet identified the exact cause of Crohn’s disease but it is believed that heredity factor plays a major role in its development. Family history of the disease seems to cause the activation of the immune system in the intestines leading to inflammatory bowel diseases. A gene associated with Crohn’s disease has been recently identified and it is called NOD2 or CARD15. Mutations in this gene increase the risk of developing Crohn’s disease.
Treatment for Crohn’s Disease
Treatment for Crohn’s disease is determined by the type and severity of the illness. The treatment mainly aims to relieve the symptoms and reduce the inflammation. Medications like anti-inflammatory drugs, antibiotics, corticosteroids and immunosuppresants are usually recommended as a first-line treatment. Surgical treatment may be necessary in patients who do not respond to medications.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...