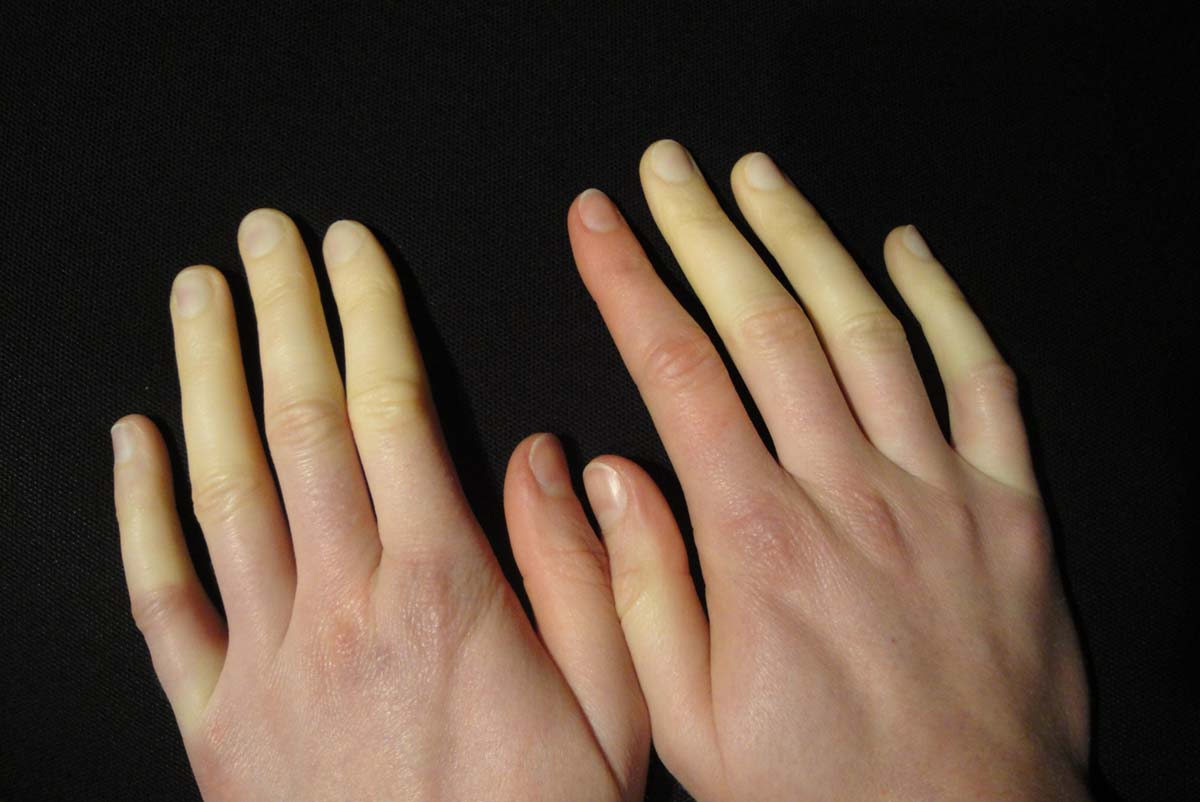
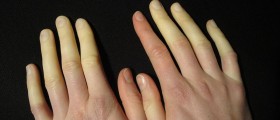
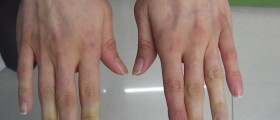
Exaggerated vasomotor response to emotional stress or temperature changes may result in a condition known as Raynaud’s phenomenon (RP). Spasm of the blood vessels in the fingers, toes and sometimes earlobes decrease the blood flow in those regions of the body and the skin changes color. At the beginning the tissue is white because of (the blood vessels') spasm, then when it starts to lack oxygen it turn to blue and when the blood vessels open again, blood in the tissue cause flushing (redness) of the skin. The sequence white blue and red is characteristic for RP.
Raynaud’s phenomenon is not a frostbite, or just cold feet and hands.
Symptoms of this condition are usually cold fingers and toes sometimes even earlobes. Sometimes RP affects other parts of the body, your nose, lips, or nipples. After the stress is gone or after warming the affected areas feel numb and thorny. Some people don’t experience all of the three colors mentioned, but the affected areas are numb and cold your sensation in them is decreased and when the blood vessels open the skin is red, and might be swollen or tingling.
Usually the Raynaud’s last less than a minute, but might be prolonged to couple of hours.
The condition might be spontaneous and without any apparent cause and then we’re talking about primary RP, or the phenomenon is caused by some certain factor. The later condition is known as secondary RP. Sometimes, the term “primary” is referring to an isolated disease, the patient is suffering only from Raynaud’s phenomenon. In that case, “secondary” means that the RP is followed with another (other) condition.
The exact reasons of the Raynaud’s condition are still unknown. Exposure to cold or hot weather and emotional stress are some of the causes related to the RP. It is suspected that RP patients have increased nerve sensitivity abnormal nerve control of the blood vessels or those small blood vessels have abnormalities in their inner wall causing the narrowing and the spasm.
Secondary RP is a condition that frequently follows rheumatic illnesses, like rheumatoid arthritis, systemic lupus erythematosus or scleroderma. Patients with carcinoid or hypothyroid condition and rarely carcinoma suffer from the Raynaud’s. Use of propranolol (Inderal), nicotine, estrogen medications without added progesterone, or other medications such as ergotamine (in migraine treatment) or bleomycin (Bleoxane) (for cancer therapy) are associated with the Raynaud’s phenomenon.
Serious case of Raynaud’s phenomenon and infected finger and toes affected with RP are the reason to consult the doctor for chronic Raynaud’s may cause skin and tissue atrophy or gangrene.








Your thoughts on this
Loading...