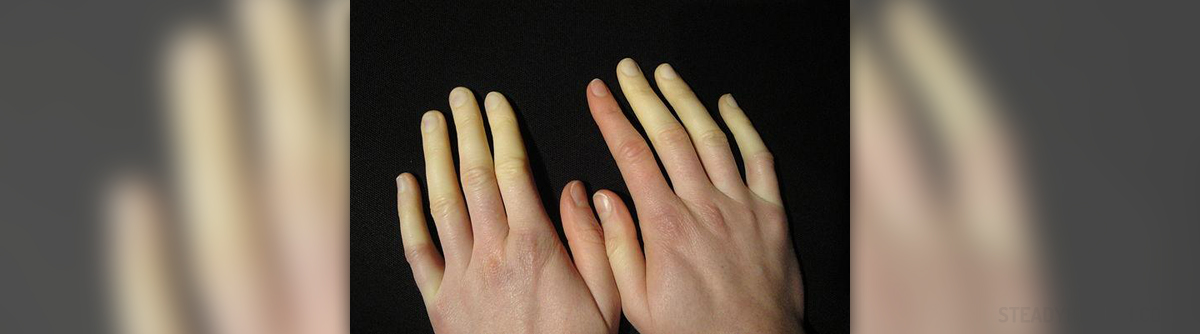
About Raynaud’s disease
Raynaud’s disease is a condition in which certain parts of the body, usually the peripheral ones like toes, fingers, nose and ears, become very cool and numb when exposed to cold temperatures or stress. In this disease, the small arteries that provide blood to those parts shrink, causing reduced blood circulation to the area, which results in a cold and numb sensation.
It would seem that people who live in cold climates are more accustomed to low temperatures and thus less prone to this disease, but the fact is that Raynaud’s is more common among them than in those who live in warmer areas. Also, this disease affects women more than it does men.
Treatment for Raynaud’s disease depends largely on its severity and on whether there are other conditions associated with it. In most cases it is more a nuisance than an actual health issue, which is why treatment is rarely indicated.
There are two main types of Raynaud’s disease - primary and secondary. In primary Raynaud’s disease, there is no underlying cause of narrowing of the blood vessels. This is the most common form of the disease.
In secondary Raynaud’s, which is also called Raynaud’s phenomenon, there is an underlying medical condition that causes the arteries to shrink. This is a more serious form of disorder and it is also much less common.
Causes of Raynaud’s disease on foot
In Raynaud’s disease the blood vessels in toes, fingers, nose, ears and other peripheral parts of the body response abnormally to stress and cold temperatures, causing a reduction in the blood flow. Although it is not completely clear why it happens, cold and stress are identified as the most significant causes of this disease.
A normal response of the body to low temperatures is to reduce the blood flow to hands, feet, ears, nose and such. This happens because the body needs to preserve its core temperature. In people with Raynaud’s disease, this normal reaction is exaggerated, resulting in extremely cold feet and hands, often accompanied by numbness.
Stress has a similar effect on the body and Raynaud’s the reaction is also exaggerated.
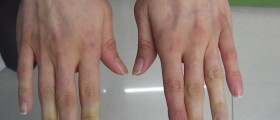
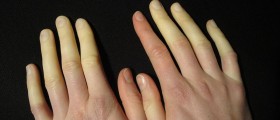
The narrowing of blood vessels is called vasospasm. When a vasospasm is triggered due to stress or cold, it dramatically cuts the blood flow to certain areas. Those areas, feet in particular, become pale or gray and cold to touch. When the vasospasm passes, the skin usually first turns red before returning to its normal color. In people who have Raynaud’s, frequent vasospasms may cause permanent hardening of the blood vessels in feet and other peripheral parts.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...