
Frostbite (medically congelatio) is the localized damage of skin or other tissues caused by extreme cold, and since a nose, chin, cheeks, ears, fingers and toes are more exposed, they are more likely to freeze. The effects and the stages can be observed on the skin which is initially cold, then becomes numb until eventually hardens and turns pale. Mild frostbites are treated by warming the skin with warm water. The numbness may leave the person unaware of the frostbite until somebody else notices the condition. Severe frostbites may harm the skin, muscles, bones and tissues, and they call for medical attention since complications that may occur includes infections and nerve damage.
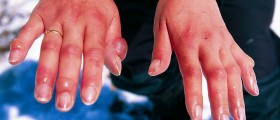
Symptoms of frostbite include coldness, burning, slight pain, tingling, itching, hard, red, pale, white or grey looking skin, clumsiness caused by joint and muscle stiffness and blisters. Frostbite starts with the frostnip which causes the skin to become cold and red, and this is followed by the prickling sensation and numbness. There is no skin damage in this first stage of the condition. In the second stage superficial frostbite occurs, and red skin turns white or pale. The skin is still soft, although ice crystals form in the tissue, while with warming, the skin turns blue or purple and blistering might ensue 24-36 hours later. The final stage is a severe frostbite which affects both the skin and the underlying tissue, so loss of sensation, numbness, pain and discomfort are prominent at this point. Joints and muscles stiffen and blistering occurs 24-48 hours after the skin is rewarmed, and the area then hardens and goes black, as the result of the dying of the tissue.
Superficial and severe frostbites require medical attention, so the affected person should report to the doctor if they are experiencing a fever higher than 100.4 F, dizziness, redness, pain, swelling or the drip from the frostbitten area, or any new, unexplained symptoms. People who have suffered frostbite, risk the occurrence of complications. They may become increasingly sensitive to cold or prone to developing frostbite again, while long-lasting numbness or nerve abnormalities may occur in the affected area. Frostbite arthritis caused by the changes in the cartilage between the joints may develop. Growth defects in children are also possible in cases where frostbite caused damage to a bones’ growth plate, as well as the infections. In most severe cases gangrene (the death and decay of tissue) can occur due to the interrupted blood supply in the affected area. Apart from frostbite, hypothermia is another danger associated with extremely cold conditions. In hypothermia body temperature is very low so the heart and the nervous system cannot operate properly. Medical attention is required to prevent heart and respiratory failure and a potentially fatal outcome.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...