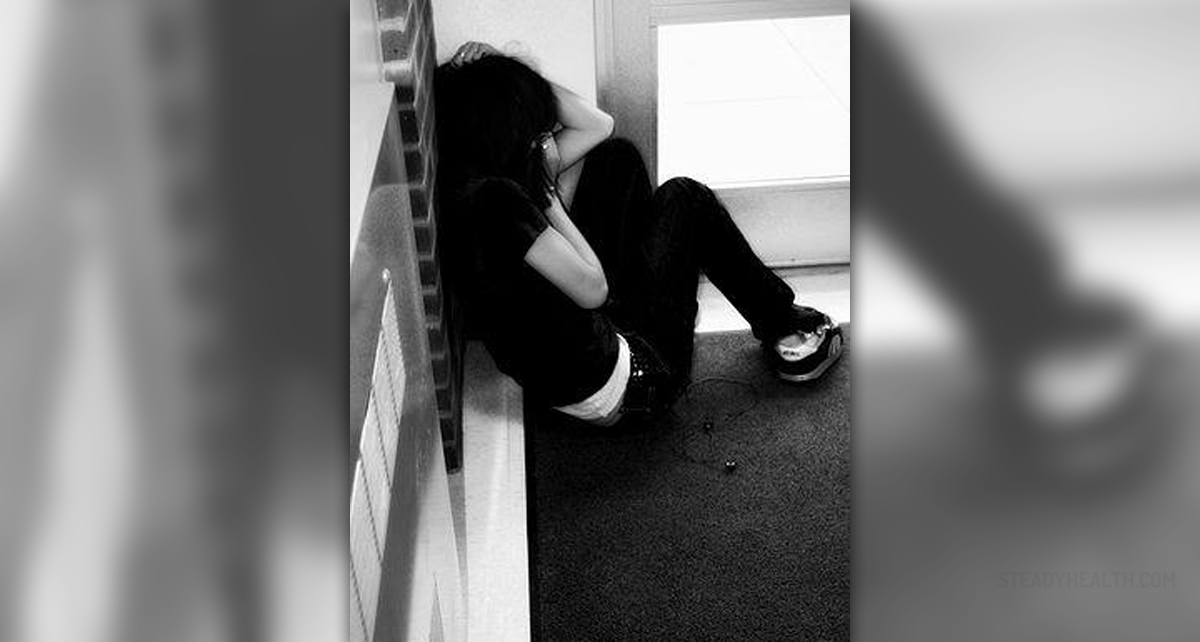

Substance abuse, or drug abuse, is a maladaptive pattern of use of a substance. People often abuse substances, which may be hazardous to their health even in the small quantities. The most commonly abused substances are drugs, alcohol, and tobacco, but people may even abuse otherwise helpful substances such as medical drugs. Most commonly, the term “substance abuse” refers to hazardous use of psychoactive substances. The final effect of substance abuse is a dependence syndrome, which is a pattern of behavioral, cognitive, and physiological phenomena that include a strong desire to take the drug, accompanied by loss of control over its use and persisting in its use despite harmful consequences. People who abuse substances usually give higher priority to drugs than to any other of their activities and obligations, and they often experience very severe physical symptoms and complications.
Social effects of substance abuse
Substance abuse is a serious public health problem that causes 2.5 million deaths each year only because of the harmful use of alcohol. About 320,000 young people between the age of 15 and 29 die from alcohol-related causes, which is about 9% of all deaths in that age group. About 15.3 million persons worldwide have drug use disorders. Smoking is responsible for nearly half-million deaths each year, and this is the most serious preventable cause of death worldwide.
Prevention of substance abuse
Preventing substance abuse requires a lot of community efforts, but it is something that can be achieved. Substance abuse can start very early in life, even during the childhood or adolescent years. Therefore, the backbone of prevention is efforts in school and community settings, focused on all age groups. Children are educated in many life skills that offer personal, social, resistance and communicational skills. Schools are also a great place to learn about negative effects of substance abuse.
Community and school-based prevention programs are carefully tailored to help the students learn to increase resistance skills in social situations that will allow them to refuse drugs more effectively. Motivational tools usually include educational handouts, lesson plans, phone support, downloadable resources, and posters, designed to increase personal and social competence, confidence and self-efficacy to reduce the effects of motivators on children.
Families are also very important and possibly the most effective way to prevent substance abuse among children is to encourage the parents to communicate freely with their children, monitor and supervise their activities and correct their misperceptions about addictive substances.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...