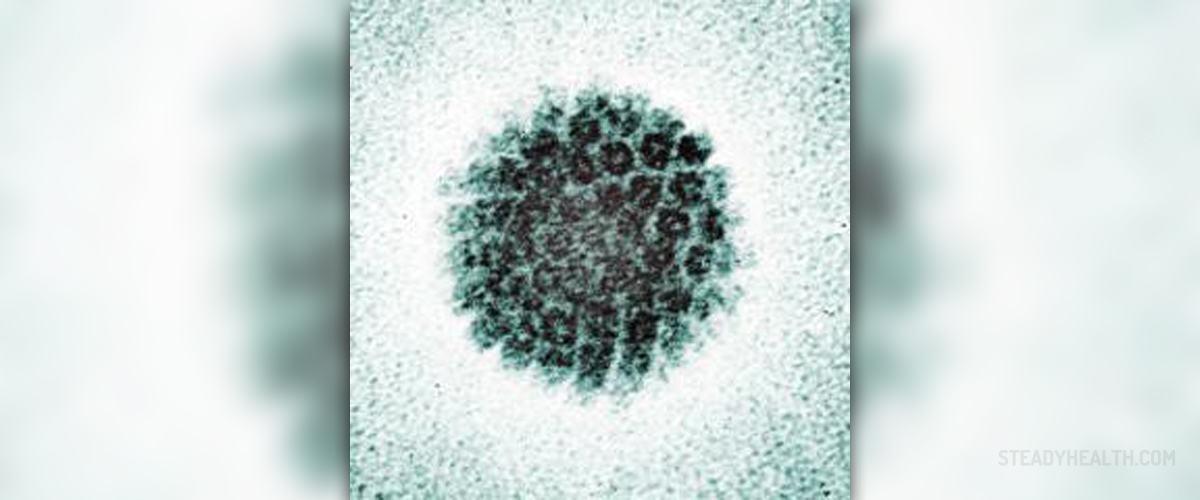
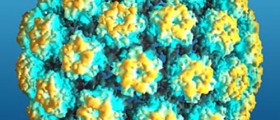
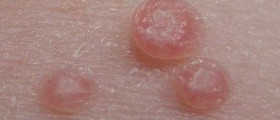
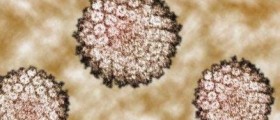
Human papillomavirus, also known as HPV, is a member of the papillomavirus family, mainly responsible for genital warts in humans. Most of the infections with human papillomavirus are completely asymptomatic and have no manifestations in humans. Sometimes they can cause warts and in a small amount of cases, they can lead to cancers of cervix, vulva, vagina, and anus in women or cancers of the anus and penis in men. Genital human papillomavirus is the most commonly transmitted sexual disease. There are many different types of these viruses and some of them can even infect the mouth and throat. When the virus causes genital warts, it usually manifests in small bumps of clusters of bumps in the genital area. Cancers caused by human papillomavirus usually do not have any kind of symptoms, until they progress to the more severe stage. For this reason, women are advised to take regular screening for cervical cancer. Other HPV-related cancers are also asymptomatic in the early stage.
How is human papillomavirus transmitted?
Human papillomavirus is usually transmitted through sexual contact. About 40 different Human papillomavirus types are known to infect genital tract, and all of these infections are transmitted during the sexual intercourse. This is why HPV infection is considered one of the most common sexually transmitted diseases. The virus is passed on through any kind of genital contact and most commonly during vaginal and anal sex. What is especially worrying is that the virus can be spread, even if the infected partner has no symptoms of the disease. This virus is sometimes passed from mother to a child during delivery. However, this rarely happens, but if it does, it may result in juvenile-onset recurrent respiratory papillomatosis. Without treatment, it is potentially fatal as uncontrolled papillomas could obstruct the airway. These papillomas are actually benign epithelial tumors.
Prevention of human papillomavirus
Regular use of condoms is generally considered good way to prevent any kind of sexually transmitted diseases. However, this does not apply to human papillomavirus, because the area around genitals also contains traces of virus, and this area is not covered by condom. Condoms can just lower the risk of HPV, but they do not offer any kind of absolute protection.
The only way to prevent the infection is to be vaccinated and lower the chances of getting HPV. Vaccines for women (Cervarix and Gardasil) are recommended for females 13 through 26 years of age. Gardasil also protects against genital warts. Only Gardasil also protects males, and it is administered for men 9 through 26 years of age.
The only way to be completely safe is to restrain from sexual activities or to be faithful with one partner.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...