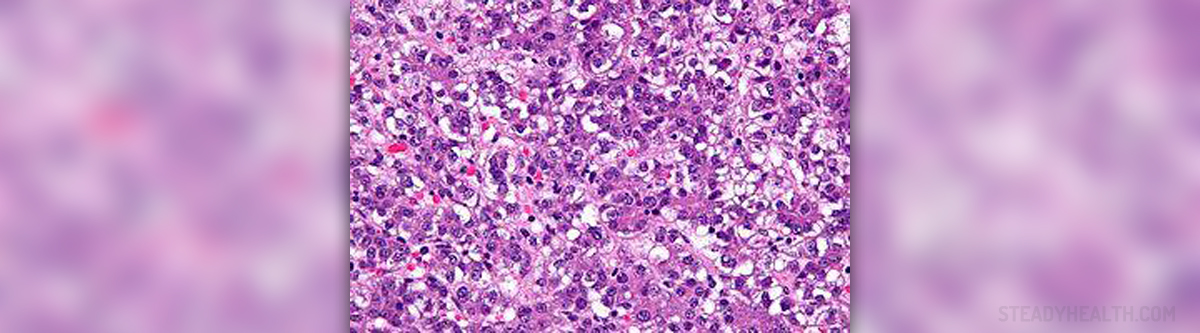
Hepatitis B is a serious infectious illnesses that affects the liver and is caused by hepatitis B virus. The course of the infection may differ and some people end up with chronic form of hepatitis B which is closely related to liver cirrhosis and liver cancer. However, many patients who contract the virus fully recover and are at no risk for chronic infection and all accompanying complications.
More about Hepatitis B
The infection leads to different symptoms and signs which range from mild to severe. They generally include weakness, abdominal pain, joint pain, loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting and jaundice. It is interesting that infants and children actually almost never develop symptoms or signs of the infection.
The virus is transmitted through blood, semen or other body fluids. Once the virus enters the body it reaches the liver and causes its inflammation. In majority of cases hepatitis B is transmitted during unprotected sexual contact. The virus can be found in semen, saliva and vaginal secretions.
Furthermore, the infection can be easily contracted by sharing needles. This is common for intravenous drug addicts. But even people whose profession is related to materials that contain the virus (particularly medical professionals) are at risk because there is always chance of accidental needle stick or other way of exposure to the virus. And finally, the virus can be transmitted from a pregnant woman to her baby.
Prevention of Hepatitis B
There are quite effective preventive measures against hepatitis B infection. The most efficient one is timely vaccination.
The vaccine against hepatitis B is regularly administered as a series of three injections. The process of vaccination is performed within a period of six months. The vaccine is safe for use in almost all groups including infants, older adults and even immunocompromised patients. One of the common side effects is soreness at the injection site. Some scientists believe that the vaccine may trigger some autoimmune disease. This, however, has not been confirmed.
Vaccination is obligatory for certain professions and is recommended in specific groups. It is suggested to vaccinate all infants, children and adolescents who have not been vaccinated and people treated for sexually transmitted diseases. Furthermore, the vaccine should be given to institutionalized developmentally disabled people, health care works who come in contact with blood and different body secretions, HIV positive people and patients with end-stage kidney disease or chronic liver disease. And finally, men having sex with men, people with multiple partners, intravenous drug users, people whose sexual partner or nearby people have hepatitis B and travelers who are planning to visit countries with a high rate of hepatitis B infection are also candidates for the vaccine.Other Means of Protection
It is good to know HBV status of all sexual partners and always use proper protection during sexual contact. The best thing is to use a new latex or polyurethane condoms. The condom does not provide with 100% protection but it significantly reduces the chance of contracting the infection. One more way to prevent infection is to stop using illicit drugs intravenously. If this is not possible, drug users should use a sterile needle each time they inject the drug.
People should also pay attention when engaging in body piercing and tattooing. It is suggested to always go to qualified and reputable shops.
And finally, before traveling to other countries one should consult his/ her health care provider and inform about the necessity of vaccination against hepatitis B.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...