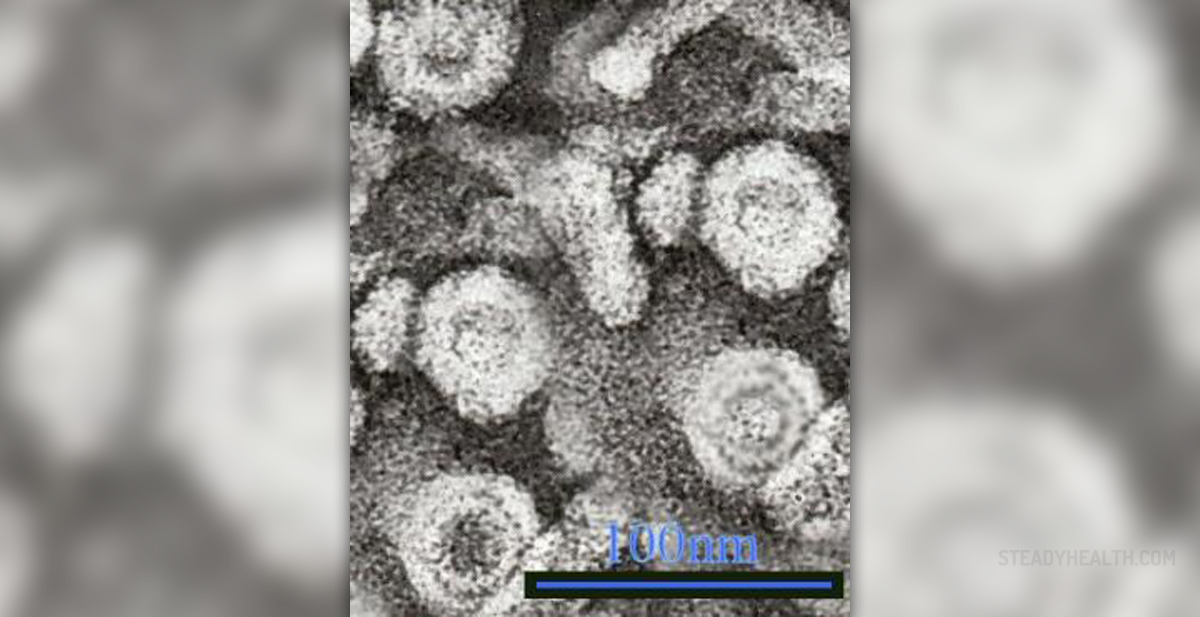
Hepatitis B is an infectious disease caused by the hepatitis B virus. This virus infects the liver and causes inflammation. This serious disease is contagious and it quite easily spreads from an infected person to other people. Hepatitis B virus already caused epidemics in certain parts of Asia and Africa. It remains endemic in China. It is estimated that about one third of world population, which is more than two billion people, have been infected with the hepatitis B virus at some point in their lives. About 350 million of these people are chronic carriers of the virus, which is the most serious form of hepatitis B infection that can eventually result in cirrhosis and liver cancer.
Symptoms of hepatitis B
First signs and symptoms of the infection with hepatitis B virus usually appear two or three months after the person has been infected. Symptoms can range from extremely mild, almost unnoticeable, to very severe. Most common symptoms include abdominal pain accompanied with nausea and vomiting. Patients usually feel very weak and suffer from constant fatigue. They can also experience joint pain and extreme loss of appetite. In most of the cases, patients will develop yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes, known as jaundice.
In some patients, symptoms of the disease will never develop. Children and infants usually fall into the group of asymptomatic patients. If any of the symptoms are present, patients should seek medical help. It is also possible to prevent the disease even after the exposure to the virus. However, this treatment must be administered within 24 hours of exposure to the virus.
Transmission of hepatitis B virus
Transmission of hepatitis B virus usually results from exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Persons usually get this virus during the sexual contact, blood transfusions, re-use of contaminated needles and syringes, and vertical transmission from mother to a child during childbirth. The risk of passing a virus from mother to a child during the birth is somewhere around 20%. The virus is commonly transmitted among the members of the same household, possibly by skin contact or mucous membranes with secretions of saliva.
Prevention and treatment
There are several vaccines available for the prevention of hepatitis B virus infection. This virus is transmitted exclusively through body fluids so means of prevention also include using the protection during a sexual intercourse. Infants can be vaccinated at birth. In most of the cases, patients clear the infection spontaneously. However, treatment is necessary for a small portion of patients, and it usually involves various antiviral medications. For severe cases, liver transplant will be necessary.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...