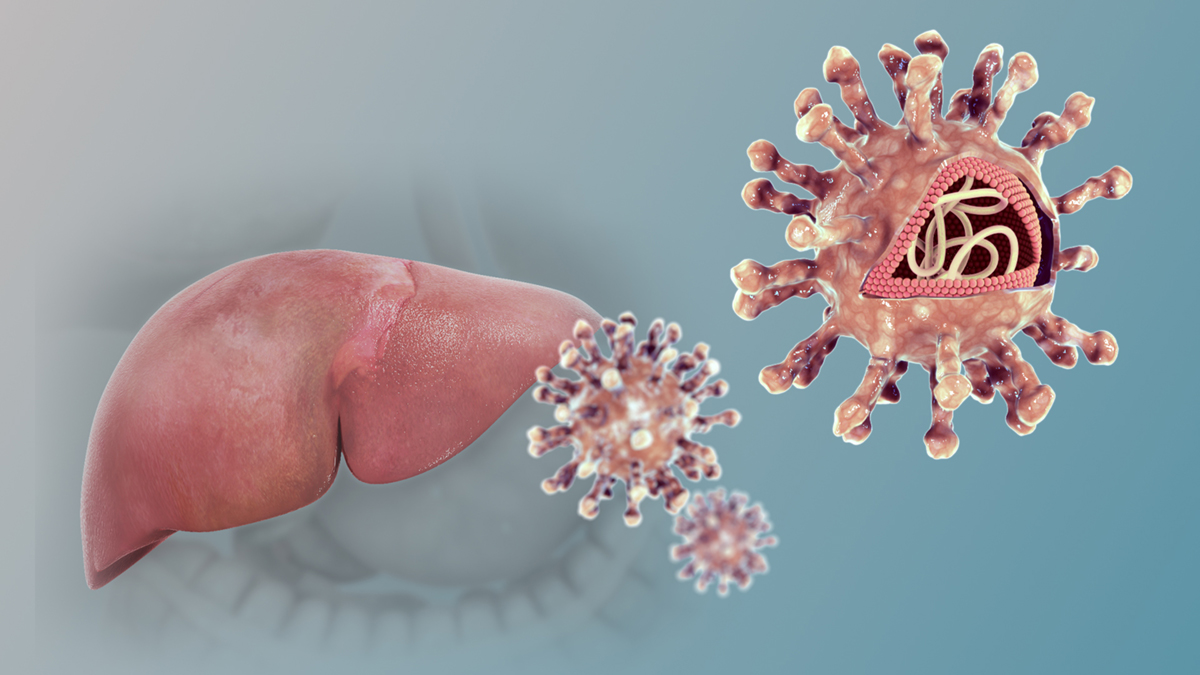
Hepatitis C is an infectious disease which affects the liver. The inflammation of the liver parenchyma is caused by hepatitis C virus which can be transmitted via bodily fluids (blood, saliva etc). This is a highly infective disease and carries many potential complications.
Hepatitis C can be classified into acute hepatitis C and chronic hepatitis C. In acute form of the disease the infection lasts approximately a few weeks while chronic form of the disease is permanent (the virus remains in the body for the rest of a patient's life). Chronic hepatitis C carries a risk of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver cirrhosis.
Transmission of Hepatitis C virus and Its Contagiousness
Hepatitis C virus is very contagious. It cannot be transmitted via droplets ejected during coughing or sneezing. The virus is secreted in bodily fluids such as blood, semen, vaginal fluids, tears, urine and saliva.
In majority of cases the infection is spread via blood (sharing of contaminated needles by drug addicts, non-sterile needles for tattoos/ body piercing). Furthermore, people working in a laboratory or a dialysis unit are at an increased risk of infection. One more way of transmission is unprotected sexual intercourse. This way of transmission is not so common but it is possible. Even sharing personal items such as razors or tooth brush can cause transmission of the virus.
On the other hand, hepatitis C cannot be spread by kissing, hugging or shaking hands. There is no confirmed data regarding transmission of hepatitis C from a mother to her baby during pregnancy or breastfeeding. There is also a little evidence regarding possible transmission of the virus via oral sex.
Symptoms of Hepatitis C
In majority of patients hepatitis C is asymptomatic until the disease progresses to certain extent. Early symptoms of infection include fatigue, nausea and tenderness in the liver area. After certain period of time patients may suffer from vomiting, low grade fever and they develop jaundice.
Treatment for Hepatitis C
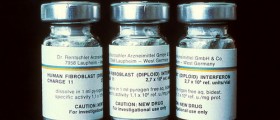
Patients suffering from hepatitis C are prescribed the special diet. They also require proper rest. If necessary they can be administered interferon. Administration of medications as well as alcohol consumption during liver inflammation is strictly forbidden. In case of chronic form of the disease patients may develop liver cirrhosis or hepatocellular carcinoma.
Since there is no vaccine against hepatitis C people may prevent themselves against the infection by avoiding sharing of needles (this rule particularly refers to intravenous drug addicts), avoiding sharing of personal items such as razors or toothbrush and proper protection during sexual intercourse (latex condoms).









Your thoughts on this
Loading...