Yellow fever is a serious viral disease transmitted to humans via a mosquito bite. This is a hemorrhagic fever that commonly affects people in certain areas of Africa and South America (both residents and travelers). Mild cases of yellow fever are characterized by fever, headache, nausea and vomiting while moderate and severe forms of the disease cause serious and potentially life-threatening bleeding into many organs such as the heart, liver and kidneys.
The condition cannot be cured but it can be prevented. People who travel to endemic countries are due to be immunized with a vaccine and this way they are fully protected against the disease.
Yellow Fever - Overview
The virus responsible for the infections is transmitted by a mosquito known as Aedes aegypti mosquito. The insect inhabits sub-Saharan Africa and is also found in South America as well as some parts of the Caribbean.
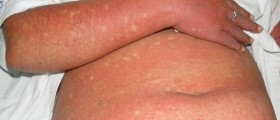
The disease is potentially fatal. It is estimated that approximately 5% of infected individuals die. Once the infection fully develops, patients complain about headaches, fever, nausea and vomiting and they start to bleed and develop jaundice.
There are two types of the infection. Jungle yellow fever is transmitted by jungle mosquitoes and it predominantly affects animals such as monkeys. Humans can get infected if they spend time in a jungle habitat, while injected monkeys may be responsible for the outbreak of urban yellow fever. Urban yellow fever is obtained by a bite of an Aedes aegypti mosquito that has bitten an infected monkey or a person already suffering from yellow fever.
Prevention of Yellow Fever
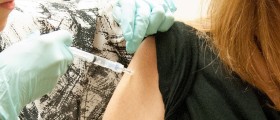
The only way to successfully prevent infection is to be timely immunized. The vaccine is highly efficient against the infection and is administered in a single dose. The protection achieved after vaccination remains for 10 years. People who have already received the vaccine are supposed to have a booster dose every 10 years, especially if they are at risk of contracting the infection.
For individuals who travel to endemic countries vaccination must be performed 10 days before the travel. The immune system requires certain time to develop immunity against the infection and this lasts approximately 10 days.
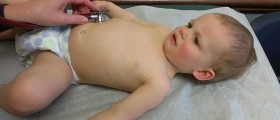
As it is the case with any other vaccine, even vaccination against yellow fever may cause some side effects. For example, a person may experience pain and swelling at the site of the injection, develop fever, complain about headache, nausea, vomiting and diarrhea. In rare occasions people may suffer from abdominal pain and arthralgia. Fortunately, these side effects are not considered serious and the protection is successfully established.
The vaccine is contraindicated in people who are allergic to eggs, children under six months of age, immunocompromised patients, children between the age of 6 and 9 months, pregnant women, breastfeeding women. The last three groups of individuals may receive the vaccine but only if the risk of yellow fever is unavoidable.













Your thoughts on this
Loading...