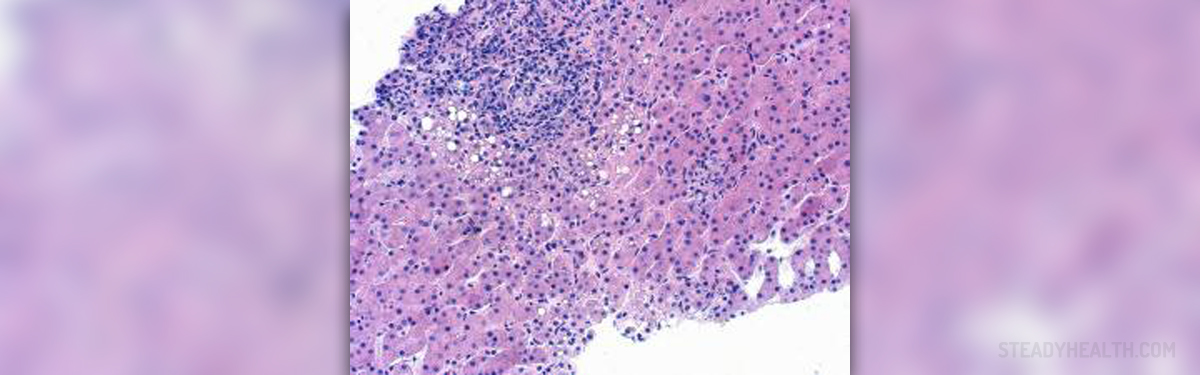
Hepatitis B is an acute and serious liver disease caused by the hepatitis B virus (HBV). The virus is found in the stool of infected patients. It spreads by exposure to infectious blood or body fluids. Symptoms
Early signs of acute hepatitis B infection resemble those of influenza or a common cold. Symptoms appear two to six weeks after the initial infection and include chronic fatigue, fever, abdominal pain, nausea, diarrhea, appetite loss, depression, and sharp pain in the upper left quadrant of the abdomen. This pain occurs because an inflamed and swollen liver puts pressure on the gallbladder. Symptoms gradually progress to the development of jaundice.
Other signs that may point to hepatitis B infection are weight loss, itching, dark amber color of the urine and light color of feces.
Course of the illness
Acute illness often lasts for a few weeks and then gradually improves. Sometimes it may show no symptoms and may go unrecognized. In a small number of patients a more severe liver disease may occur, the so called fulminant hepatic failure. Severe complications might appear rapidly and cause severe damage to the liver functions. Liver transplantation is often required in patients suffering from acute liver failure. However, some of the patients may die because of the failure.
Chronic infection may also be asymptomatic or may be associated with a chronic inflammation of the liver. This type of infection gradually progress to liver cirrhosis and it may significantly increase the risk of liver cancer.
Treatment and Prevention
Vaccine named Engerix-B is used to prevent hepatitis B infection. It stimulates the body to produce antibodies against infection.
Persons allergic to any of the ingredients, including yeast or mercury, as well as those who already had an allergic reaction to this vaccine in the past, should not use Engerix-B. Patients should consult with their doctors before taking Energix-B, especially if they are pregnant or planning pregnancy, taking medicines, allergic to medicines, food or other substances, or having a weakened immune system.
Side effects of the vaccine
Hepatitis B vaccine is usually well tolerated. Side effects are usually very mild and include fatigue and local irritation on the injection site. Other side effects may include fever, chills, flushing, lightheadedness, sweating, weakness, malaise, tinnitus, and earache.
Respiratory side effects that might show up are hinitis, cough, pharyngitis, upper respiratory tract illness, influenza-like symptoms, and bronchospasm including asthma-like symptoms.
Some of the side effects show up on nervous system. Those include headache, dizziness, vertigo, somnolence, insomnia, irritability, agitation, migraine, syncope, paresis, neuropathy, hypoesthesia, paresthesia, convulsions, encephalitis, Guillain-Barre syndrome, radiculopathy, herpes zoster, muscle weakness, multiple sclerosis, and exacerbation of multiple sclerosis, Bell's palsy, optic sclerosis, myelitis, and transverse myelitis.
Musculoskeletal side effects may show up as arthritis, arthralgia, myalgia, back pain, and pain or hardness in the arm, shoulder, or neck.
Some of the side effects may affect liver, and show up as abnormal liver function tests. Side effects may also be hematologic and cause lymphadenopathy, thrombocytopenia, and increased erythrocyte sedimentation rate. Cardiovascular side effects usually include syncope, hypotension, tachycardia, and palpitations.
Gastrointestinal side effects are not so rare and they include diarrhea, nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, cramps, anorexia, constipation, and dyspepsia.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...