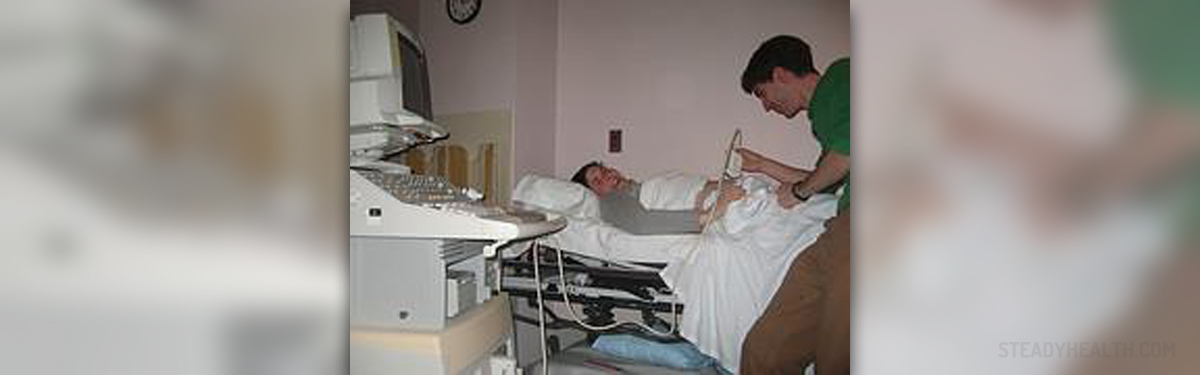
Abdominal Ultrasound Facts
How is the Procedure Done?
Preparing for ultrasound testing is relatively simple. It is advised that comfortable clothing be worn and jewellery left at home. The patient will be asked to take the clothes off and put on a disposable paper robe. The patient is asked to lie on a bed during the test. In many cases he or she will have to change positions to allow the technician to get a good look. The test is performed either by a trained technician or by a radiologist. The ultrasound exam rarely takes more than half an hour. Depending on the organ that is being examined in the abdomen some of the preparatory steps may differ. For instance, for the aorta ultrasound it is recommended that the patient does not eat 8 to 12 hours prior to the exam. In the case of kidneys the bladder has to be full in order to get the most optimal results. Also, some patients will be asked not to eat for 8 to 12 hours before the ultrasound to avoid gas build up in the intestines which can obstruct the view and skew the results. When it comes to examining pancreas, gallbladder, spleen, and liver it is best to eat a fat-free dinner the night before as well as not eat for 8 to 12 hours before coming for the ultrasound. In addition, ultrasound consists of a transducer, computer, video screen, and electronics. The transducer is the tube which is rubbed against the abdomen in order to release the sound waves. Before beginning each test, the technician will put some gel on the patient’s abdomen to facilitate the process. The transducer receives the echo for the organ in question and interprets in on the video screen. The principles of ultrasound are similar to those of the submarines. When the sound waves hit the object in question they produce an echo. The echo reveals the size and shape of the object. As a result, the doctors are able to detect changes in the appearance of organs, vessels, and tissues, as well as notice tumors. The image is available on the screen right away, and the results are often discussed immediately. The printouts together with the official report are sent to the referring specialist within a few days.Aortic Aneurysms
One of the very common reasons for having an abdominal ultrasound is a possible aortic aneurysm. In case the results come back positive there are certain steps that need to be taken. If the aneurysm is relatively small, i.e. smaller than 5 cm, the doctor will probably recommend regular monitoring every six months. If the aneurysm is larger the best treatment option is surgery. The doctor would need to open the abdomen, remove the portion of aorta that contains the aneurysm and replace it with a tube-like graft. There is also a procedure called endovascular stent graft during which the crippled part of the aorta is strengthened with a graft similar to that used in the open aneurysm surgery.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...