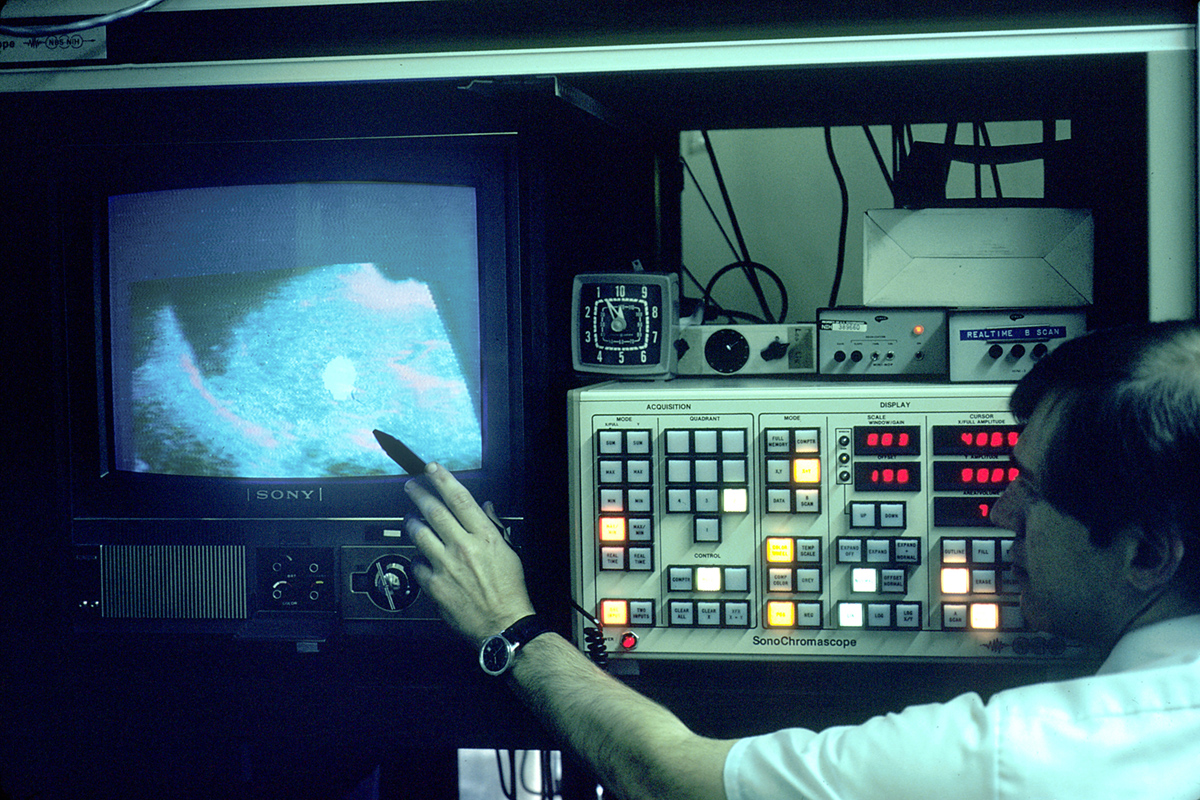

Abdominal Ultrasound
Ultrasound is a scanning technique used to evaluate the state of internal organs. One of the most common areas for ultrasound testing is the abdomen. The principles of ultrasound are similar to those of the submarines. High frequency sound waves are emitted through a tube called transducer into the abdomen. Once the waves hit the object an echo is produced and the images are revealed on a screen. Based on the echo the person administering the test is able to assess the shape and size of the organ as well as notice any masses of cells such as tumors. In addition, the organs that can be evaluated using the abdominal ultrasound include liver, gallbladder, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, bladder, and the abdominal aorta. In most cases the ultrasound is not invasive and is therefore painless. Transvaginal and transrectal exams involve penetration and are also used for extracting cells to be tested for pathological changes. Blood flow, veins, arteries, and blood vessels can also be analyzed using a special ultrasound technique called the Doppler effect. A radiologist is able to insert a dye into the patient intravenously and follow it as it makes its way from organ to organ through the blood stream. It should be noted that unlike X-Rays, ultrasound does not emit radiation and does not expose the patients to any adverse effects.When To Get Ultrasound?
Medical care providers will send patients for ultrasound if they are complaining of a number of different symptoms. For instance, those who are suffering from unidentified abdominal pain are likely to be referred for an ultrasound exam. Individuals who are over 65, are smoking, and are also suspected of having an aneurysm in the aorta will also be sent for an ultrasound. The test may be recommended for liver checkups or diagnosing jaundice, cirrhosis, fatty deposits, or overall functioning of the liver. Inflammation of the gallbladder or the presence of stones can also be determined, and so can the obstruction of bile ducts. Fluid build up in the abdomen can also be detected. Ultrasound is used to guide the needle during the extraction procedures to remove the excess liquid or during biopsies. Ultrasound is also able to differentiate between cysts and tumors in internal organs. Obstruction of urine flow in kidneys and bladder can also be determined using ultrasound. Possible causes of repeated urinary tract infections can also be discovered. The person’s reaction to therapy is also manifested through ultrasound. When organs are transplanted the recovery is followed via ultrasound. Any changes on the spleen and pancreas are easily determined as well.How To Prepare
Preparation for ultrasound examination is relatively simple. In the case of abdominal ultrasound the bladder needs to be full in most cases in order to get the reliable results. The test will be performed before and after voiding and the results compared to determine whether there are any significant changes. Eating a fat free dinner the night before the test is recommended for pancreas, gallbladder, liver, and spleen ultrasound. Valid results are also obtained if the person does not eat 8 to 12 hours prior to the test. The same type of food restrain is advised for the aorta ultrasound. In the case of kidneys patients are advised not to eat for the same period of time to avoid any gas build up in the intestines that might obstruct the view. The bladder needs to be full for the kidney ultrasound.What to Expect












Your thoughts on this
Loading...