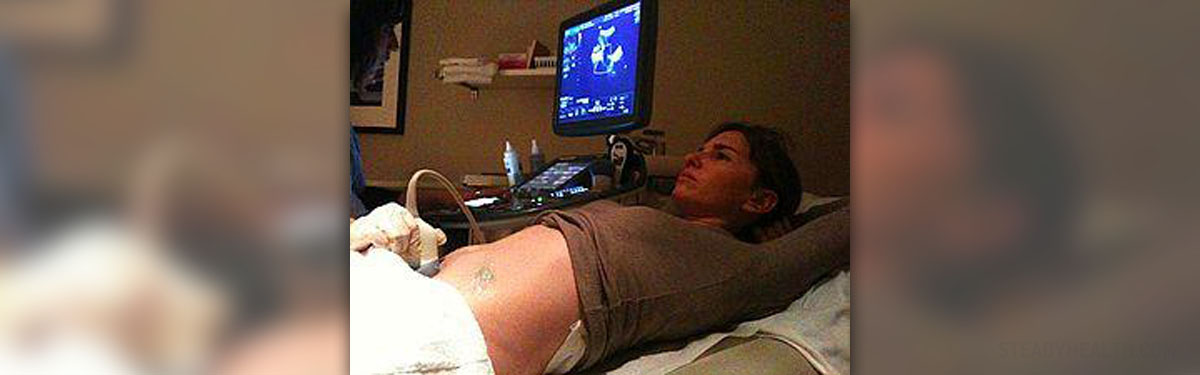
Ultrasound of the Bladder
Ultrasound is a type of image testing during which the doctors are able to follow real time state of the patient and print out the results immediately. Ultrasound uses high frequency sound wave to generate images, and it is a safe and painless exam. Compared to X-Rays which emit radiation, ultrasound does not expose the patients to any negative effects. In order to get the best results of the abdominal ultrasound it is advised that the bladder be full. Similarly, when going for a bladder exam the most accurate results are obtained with a full bladder. Individuals are sent for bladder ultrasounds if they exhibit urination problems. One of the things available from the bladder ultrasound is the shape and size of the organ, the amount of urine the person can hold, as well as whether the individual empties the whole bladder when voiding. Other elements that become obvious during the exam are the thickness of the walls of the bladder and the presence of any stones or cysts.
ProcedureThe preparation for the test is not complicated as it only requires drinking plenty of liquids. Parents are advised to explain the procedure of the test to children so that the ultrasound is performed smoothly and accurately. Children are sometimes scared of the big machinery and often need to be encouraged by the care givers. Explaining to them the steps of the test as well as the reason for doing it in the first place is very important so ease the anxiety. Empathy and understanding will help the child relax, which in turn makes the muscles less tense and results more accurate. The exam is administered at a radiological center or hospital by specialists called radiologists or by trained technicians. Prior to the test patients are told to take the clothes off and put on a disposable paper robe. It is advised that comfortable clothing be worn and jewellery left at home. The patient lies on the table in a dark room where the images on the screen can be seen clearly. The person administering the test will put gel on the lower abdomen of the patient in order to ease the transmission of sound waves. The ultrasound machine consists of a transducer, computer, visual screen, and electronics. The transducer emits the sound waves and interprets the echo from organs which are being examined. It is rubbed on the abdomen and live streaming is available on the screen for analysis. Upon examining the full bladder the patient will be asked to empty it and come back for more testing. The two types of images are compared when making diagnosis. Ultrasound of the bladder should not take more than half hour. In addition, no pain is felt during the test. Slight discomfort is present as the technician is pressing the transducer against the full bladder but as the test is not invasive the nuisance is minor. The patient may be asked to switch positions while lying on the table and hold their breath for short periods of time. Upon completion of the test a radiologist will interpret the data and send them to the referring physician. The referring doctor may be able to formulate a diagnosis based on the ultrasound alone or further testing will be scheduled. In most cases patients wait for a few days for the results, but if the data are needed urgently they can be obtained relatively quickly.
Are There Any Risks of Ultrasound Scan?
There are no known risks associated with bladder or most other types of ultrasound. As there is no radiation no effects are left on the patient. On the other hand, trasvaginal and transrectal ultrasounds are invasive tests, which are also used for obtaining small tissue samples from vagina in women or prostate of men. The test is somewhat painful and is sometimes administered under a local aesthetic. If larger amounts of anesthetics are given the heath, breathing, and blood pressure can be affected. Minor bleeding can also be expected from extracting cells to be tested for pathological changes in the organs.Renal Ultrasound Imaging
Renal ultrasound is used for evaluating the kidneys. Individuals who might have kidney stones are sent for an ultrasound as they can easily be revealed. Various types of both kidney and bladder infections can be detected though ultrasound. Genetic anomalies of the renal tract are also visible and so are prostate problems. In case injury or trauma is sustained ultrasound is used to assess the damage. Similarly to bladder ultrasound, in order to acquire valid and reliable results the patient needs to fill the bladder prior to a renal exam. The procedure is for the most part identical to that of the bladder testing. The results are discussed right away, while the official report is sent to the referring physician within a couple of days.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...