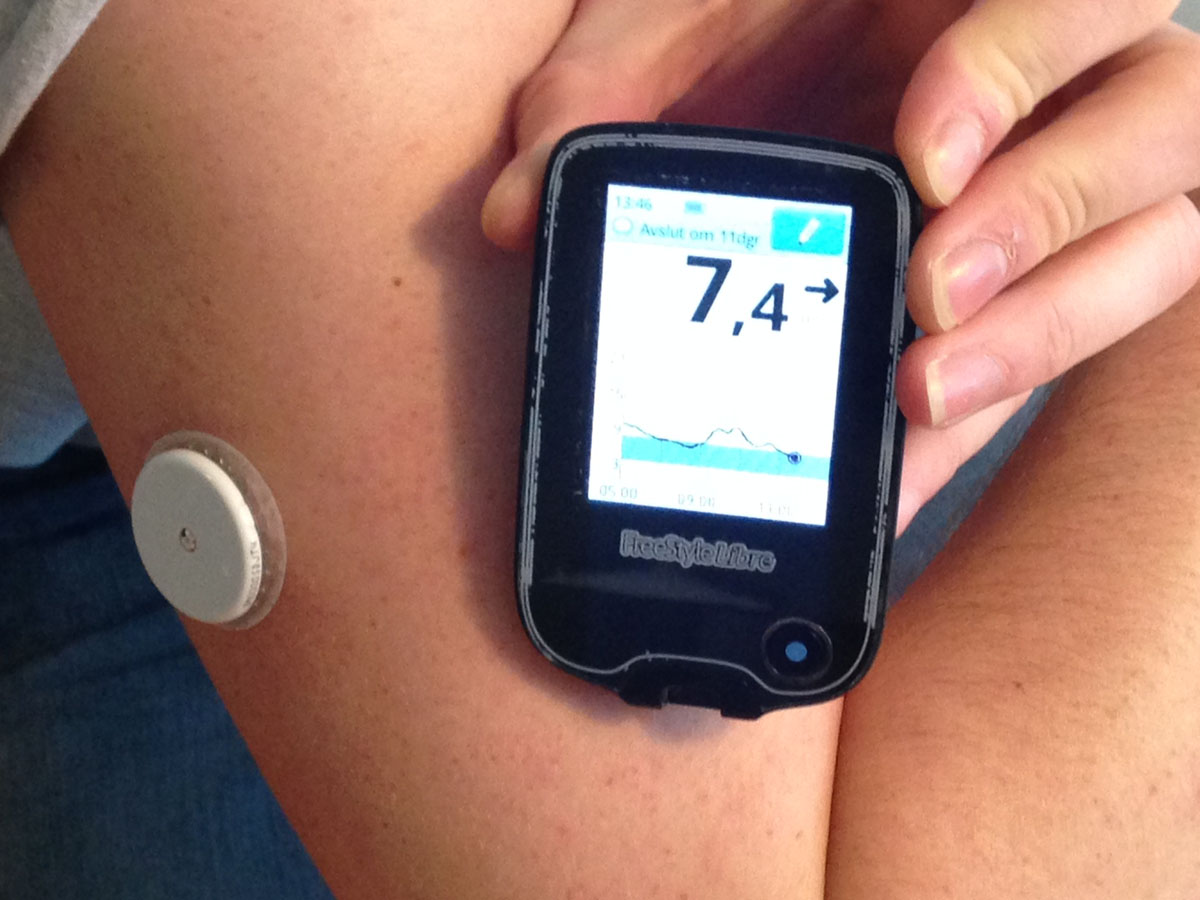
Pre diabetes?
Pre is Latin for "before", and is used to indicate that we are referring to something that has come to pass or is happening before something else. To make it simple, "pre diabetes" means "before the onset of diabetes". Medically, this refers to a state where blood sugar levels are higher than they should be, but they are still not enough to call the condition diabetes. The "pre diabetes" condition is also known as impaired fasting glucose (IFG) or impaired glucose tolerance (IGT).
People who are affected by this condition will likely develop type 2 diabetes. The elevated level of blood sugar will gradually cause long term damage to the body, such as cardiovascular diseases, strokes and eye damage. What is really nasty about pre diabetes is that it shows no signs of its presence, as there are no telltale symptoms. So, most people who have pre diabetes have no clue what is going on and might be riding the silent train to type 2 diabetes station.
Who can get it?
Pre diabetes typically affects people who have a family history of diabetes (they probably have a genetic predisposition for diabetes) and overweight people. Other high risk groups include people with low or absent physical activity, high blood pressure, then, women who suffer from polycystic ovarian syndrome and women with a history of cardiovascular diseases. A periodic pre diabetes test, once every two to three years, is recommended to such people.
Why it happens: the mechanism
Carbohydrates that we eat are absorbed into the system from the intestines in the form of simple sugars, and glucose is the most common of them. It is of little use in blood, it needs to get into cells to be either used right away as a source of energy or converted in some form more suitable for later use such as glycogen, or a triglyceride (that is, a lipid, that is, fat). A hormone produced by the pancreas, called insulin, helps glucose to get from the blood in the cells. If there is either too little produced insulin (or too much glucose in the blood), or if the cells become insulin-resistant, that is, non-responsive to the effect of insulin, then the glucose levels in blood rises, gradually leading to damage to the blood vessels in the kidney, heart and eyes.
Pre diabetes treatment
Goal of the treatment is to bring glucose levels back to normal before there is any damage. In example, it has been shown that reduction of body weight for as little as 5 - 7 percent greatly reduces blood sugar levels in obese people. Such diets, when matched up with a healthy lifestyle and a proper meal plan can help to reduce pre diabetes blood glucose levels.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...