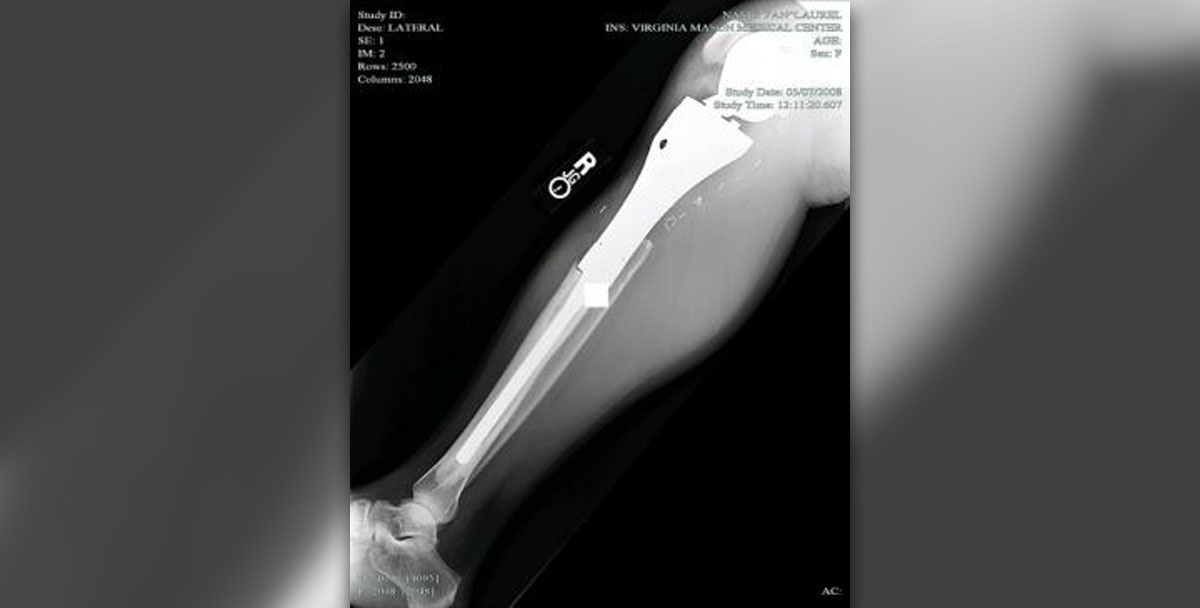
What is the tibia?
This bone, which is scientifically called the tibia, is located on the frontal part of the lower part of the leg, below the knee. This bone, in fact, serves the purpose of connecting the knee bone structure to the bone structure of the foot. So, it is not difficult for you to imagine that great stress is put on the tibia bones, especially during forceful physical activities, but even as you walk.
The fact that the tibia is constantly exposed to stress during sports activities is also why injuries of the tibia are tightly associated with the everyday life of sportsmen and women. So, the most frequent injury is the breakage (fracture) of the bone, in fact, that is an injury that is caused by excessive physical stress.
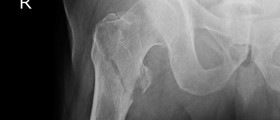
However, the biggest problem is that the indicators of this injury are very similar to any other injury near the tibia bone, such as, for example, the inflammatory process of the nearby tendons. Because of that, the first step of your treatment is to determine if you have sustained a tibia fracture. Although a doctor can assess this during a physical exam, you will also need an X-ray.
Tibia pain: A description of the pain and the treatment
Unfortunately, among all the indicators and symptoms of a broken tibia, (sometimes severe) pain is the most prominent one. On the other hand, this pain is rarely felt when the person is motionless. It is, however, characterized by a gradual increase, especially if even bigger pressure and stress is put on the tibia bone. Besides the pain, many people will find that a numbing of sensation is also present, as well as a lack of strength (as in, you will not be able to do the same activities) and the appearance of the swelling over the affected spot.
Under a hard pressure, the pain emerges from the inner side of the calf muscle and the pain is also aggravates if the nearby area is tapped. Sometimes even a hard lump-like formation could emerge from the tibia bone. So, if the pain isn’t centered and localized, there is not the case of the tibial stress fracture, unlike in the case of the inflamed nearby tendons (which is also, however, characterized by the pain that gradually increases).
Nevertheless the greatest mistake one could do is to neglect a painful tibia bone and after some period continue with the regular workouts or activities, mostly because the pain is not present in the periods of inactivity. Since this type of injury is the logical consequence of using this bone beyond its limits, the harmful habit of exercising too much must be replaced first of all. Also, one factor that can contribute to causing this kind of injury could be a lack of the essential minerals for the bones, which are magnesium and calcium, or of some proteins, or even if there is a little concentration of the sex-hormones in the organism.
The period of the rehabilitation usually lasts from 3 months to a half of year after a tibia fracture, but in the more severe cases, it is recommendable to prolong the period up to whole one year. Physical rehabilitation may help you recover faster. While you will be able to return to normal every day activities quite soon, athletic pursuits will need to be delayed until your doctor tells you that you can resume.







Your thoughts on this
Loading...