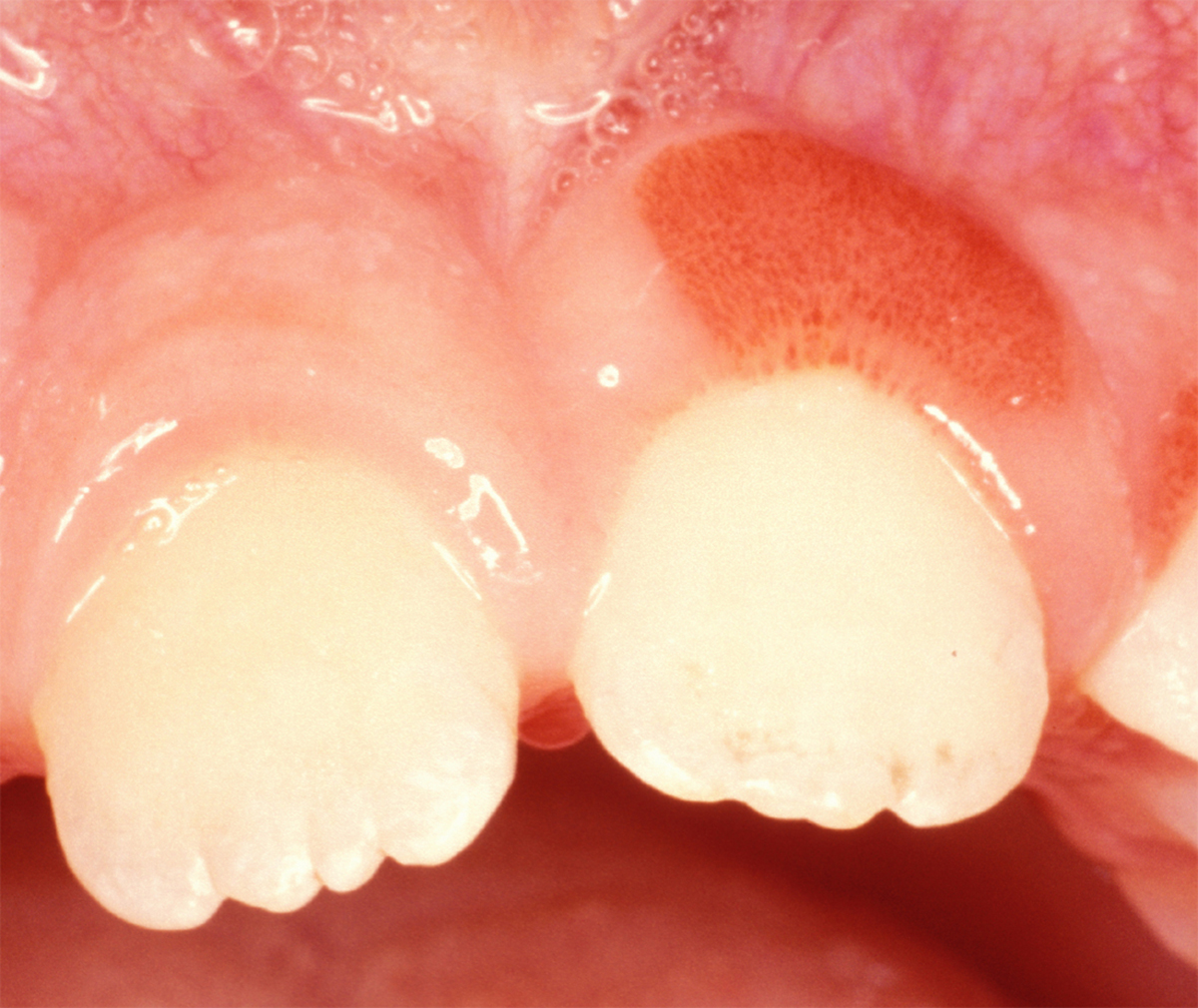
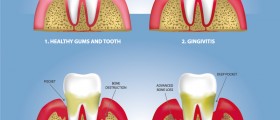
Gingivitis is an inflammation of the gum. It features with swelling, redness and bleeding from the gum. The condition is additionally accompanied by the pain or at least discomfort. The diagnosis can be easily set by simple inspection of the gum. The treatment of gingivitis includes professional cleaning of the teeth and enhanced dental hygiene. Many people mistake and while suffering from gingivitis tend not to brush their teeth since it causes bleeding. However, this only makes the situation worse and leads to even greater inflammation. In rare cases the patients require medications and in extreme cases the disease is treated even surgically.
Gingivitis should be treated on time. Each and every person must pay attention onto the oral hygiene and prevent gingivitis. The prevention of this inflammation is actually a perfect prevention from consequent and even more serious conditions such as periodontitis.
The actual cause of gingivitis in majority of cases is poor oral hygiene. It results in accumulation of plaque between the gingiva and the teeth. The plaque leads to irritation and if accumulated enough the plaque can even lead to formation of gingival pockets. Gingival pockets are an excellent place for multiplication of bacteria and accumulation of food and this is what causes irritation of the gingiva and its inflammation.
Apart from poor oral hygiene the person can develop gingivitis due to other conditions including malocclusion, food impact, Xerostomia and many more. It can also affect women during menstruation and pregnancy or in menopause. This inflammation can represent one of the signs of some other medical conditions such as leukemia, AIDS, diabetes or vitamin deficiencies.
Symptoms and Signs of GingivitisThe first signs are connected to inflammation. Gums are red, inflamed and swollen. They bleed if touched or spontaneously, and the patient complains about the discomfort or pain.
In pericoronitis the pain always accompanies inflammation of gingiva. In this case the disease is complicated by infection and eventual formation of an abscess.
Desquamative gingivitis can develop in menopause. It features with red and extremely painful gingiva. The bleeding is easily induced. In this type of gingivitis the gingiva eventually becomes covered in vesicles which rupture and lead to desquamation.
In pregnant women the gum may be swollen and the edema predominantly affects interdental papillae. In the first trimester the woman may suffer from pedunculated gingival enlargement which will withdraw after the delivery. In some cases the gingival growths do not withdraw completely.
In diabetes gum can get infected and the formation of abscesses is common. Gingival enlargement featured with redness and bleeding can be also a characteristic of leukemic infiltration.
And finally, symptoms of vitamin C deficiency include hyperplasic and inflamed gingiva which bleeds rather easily. Similar symptoms affect people who are suffering from niacin deficiency.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Gingivitis
The diagnosis is set after inspection. Still the doctor will have to look for underlying cause of gingivitis and to treat both, the cause and gingivitis itself.
A person requires professional cleaning and adequate oral hygiene. In case of excess of gingiva, it will be excised. If the cause of gingivitis are certain medications, they are to be discontinued. In pericoronitis the doctor removes the debris from under the gingival flap. If gingivitis is severe the patient may even be prescribed antibiotics.







_f_280x120.jpg)





Your thoughts on this
Loading...