Nervous System Involvement in Behcet’s Disease
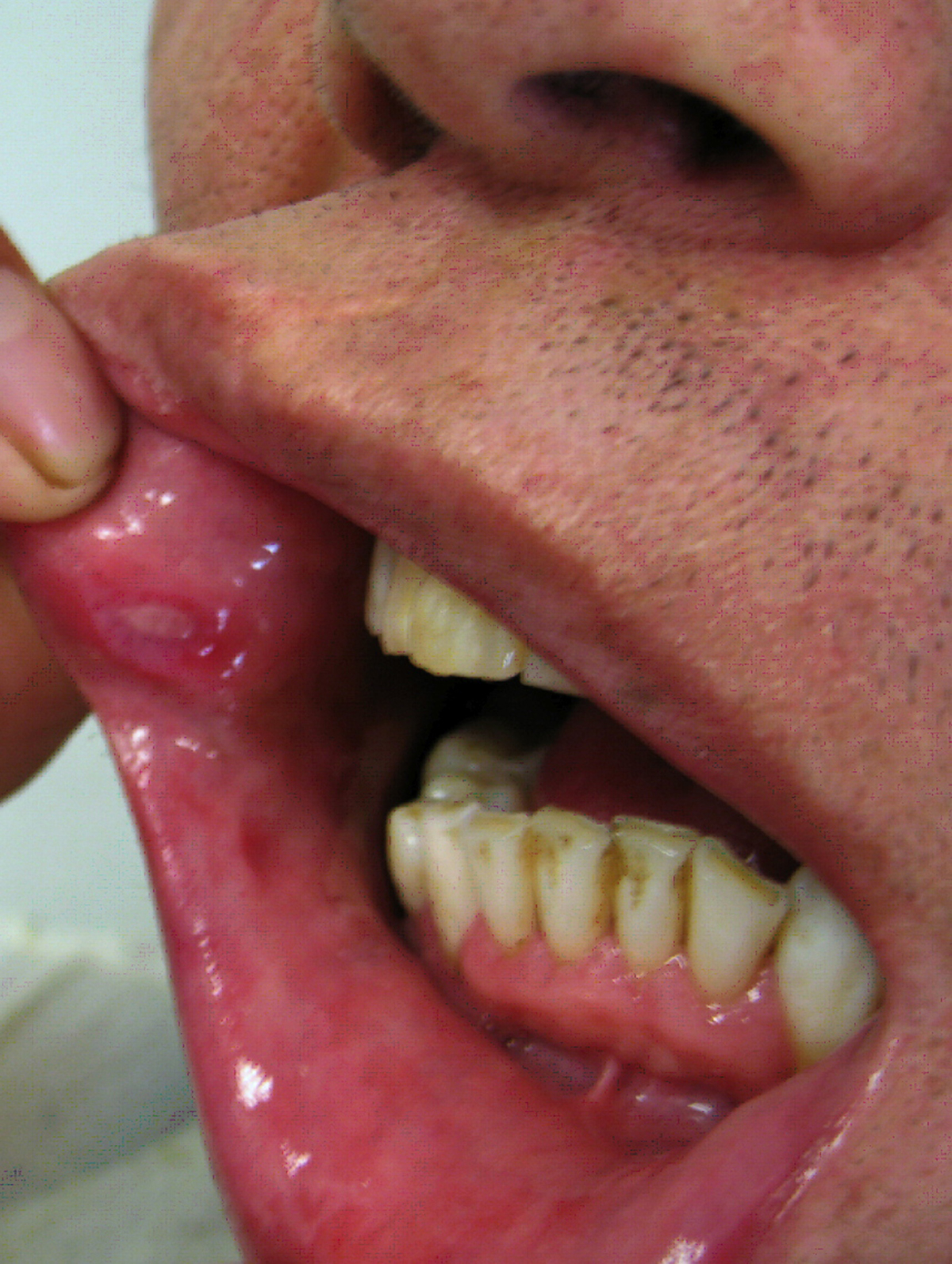
It is a well known fact that those who suffer from Behcetdisease may also suffer certain types of neurological medical problems whichmay be related in an indirect or direct manner. The most common ones, which areusually considered as direct effects of Behcet disease include a non structuralrecurrent vascular type headaches and cerebral venous sinus thrombosis. Those whoconsidered to be related to the Behcet disease in an indirect manner includeneurologic complications, depression and tension type headache. Some rare casesof Behcet disease may also include certain peripheral nervous systeminvolvements. Other involvements related to the nervous system may includecoincidental neurological involvement, secondary neurological involvement,complications of treatment of Behcet disease and Neuro-psycho-Behcet syndrome.
Diagnostic Criteria for Neuro-Behcet Syndrome
There are certain criteria which need to be fulfilled sothat the neuro-Behcet syndrome can be diagnosed properly. First of all, theInternational Diagnostic Criteria for Behcet’s disease needs to be fulfilled. Aperson needs to suffer from certain neurological symptoms which cannot beassociated with any other type of neurological or systemic disease. The personwho is about to be diagnosed with Neuro-Behcet syndrome also needs to show atleast one of the following: abnormal neurophysiological studies which arealways in consistence with the current neurological symptoms, abnormal cerebrospinalfluid findings suggestive of Neuro-Behcet syndrome, abnormal neuroimagingfindings suggestive of Neuro-Behcet syndrome or objective abnormalities onneurological examination. As already explained, the two major neurologicalpresentations of Behcet’s disease are the cerebral venous sinus thrombosis orthe central nervous system involvement. The cerebral venous sinus thrombosis iscommonly related to an increased intracranial pressure, while the centralnervous system involvement usually includes certain cortiospinal tractsyndromes or brainstem syndromes. Cerebral venous sinus thrombosis is also referred to as extra axial NBS,while the central nervous system involvement may also be referred to as intraaxial NBS.
Diagnosis of “Headache” in Patients with Behcet’s Disease
There are various types of different headaches which can bediagnosed in persons who suffer from Behcet’s disease. They include co-existingprimary headaches such as tension type headaches or migraines, the nonstructural headaches of Behcet’s disease, headaches in associated with ocularinflammations, headaches due to cerebral venous sinus thrombosis and headachesdue to central nervous system parenchymal involvement. Headaches are actuallythe most common neurological symptoms among people who suffer from Behcet’sdisease. There are cases of Behcet’s syndrome which are characterized by aparoxysmal migraine like headaches which may be frontal or bilateral and theirthrobbing and severity may vary from person to person. These headaches usuallyoccur when all other systemic symptoms of Behcet’s disease start kicking aswell. There are also certain cases whichmay be associated with rather severe headaches, and all of them usually requirefurther evaluation.
Statistical Data
According to certain statistical data from the Behcet’sDisease Research Center the range of patients affected by nervous systeminvolvement in Behcet’s disease is somewhere between 2.2 and 49 percent. Thereported mean age of onset of Behcet’s disease is 26.7, while the reported meanage of onset for nervous system involvement associated with Behcet’s disease is32 years. It is a peculiar fact that various different types of neurologicalcomplications associated with Behcet’s disease affect male patients much moreoften than they affect female patients. The ratio of male to female patientswith Behcet’s disease is somewhere around 3.8 to 1, while the ration of male tofemale patients whose condition is accompanied by nervous system involvement issomewhere around 1.8 to 1. The male predominance is also noted in cases ofother sorts of vascular complications of Behcet’s disease.
Intra-axial NBS and Extra-axial NBS
Intra-axial NBS involves the onset of certain subacute brainstemsyndrome which is commonly characterized by mild confusion, unilateral orbilateral corticospinal tract signs, dysarthria and cranial nerve findings. Itis very rare to find any cases of NBS which are not accompanied by oral ulcers.A peculiar fact is that not all intra-axial NBS cases involve brainstemsymptoms and signs. Some less common cases of intra-axial NBS may also involveextrapiramidal seizures and signs, a progressive or self limited myelopathy,emotional lability, cognitive-behavioral changes and hemiparesis. Various sortsof voiding dysfunctions which affect the sphincteric components and the bladdermay also be present in some cases. There are approximately 15 percent of casesof Behcet’s disease which are accompanied by cerebral venous sinus thrombosisas a neurologic involvement. This involvement may be characterized by certainsymptoms such as moderate headaches, motor ocular cranial nerve palsies, mentalchanges and in some cases even severe headaches. This type of thrombosis neveroccurs suddenly as it takes some time to develop fully. Some cases withcerebral venous sinus thrombosis may be accompanied by severe symptoms such ashemiparesis, sixth nerve paresis, papilledema, focal neurologic signs, coma,paralysis and convulsions.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...