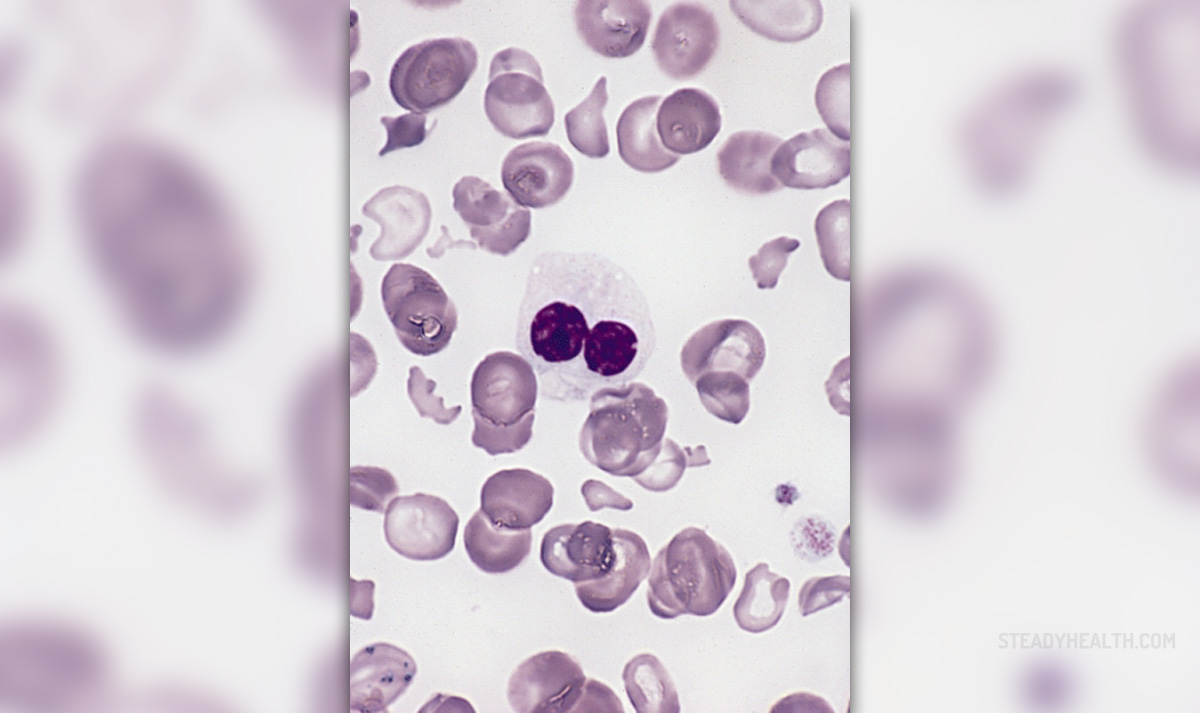
Antiphospholipid or Hughes syndrome is an autoimmune disease that is characterized with the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies associated with the occurrence of arterial and venous thrombosis (blood clots), repeated spontaneous abortions, premature births and thrombocytopenia (reduced number of platelets ).
The disease is known as a sticky blood syndrome, and it was first described by British rheumatologist Dr Graham Hughes in 1983 in the British Medical Journal. The term primary Antiphospholipid syndrome is used when the disease appears independently. If it occurs in parallel with other autoimmune diseases (such as systemic lupus erythematosus) then it is considered as secondary Antiphospholipid syndrome. In rare cases occurs complications such as generalized thrombosis and subsequent massive cancellation of body organs, when the disease is called a catastrophic Antiphospholipid syndrome.
Cause of this disease is not fully known. Antiphospholipid antibodies reduces the level of protein that binds phospholipids and has a strong anticoagulant effect, increasing the tendency to blood clotting and abortions, characteristic for this condition.
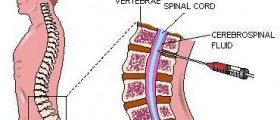
Patients with Hughes syndrome are prone to thrombosis , which can affect the functioning of almost all organs. Usual consequences of this syndrome are: abnormal blood clotting in the arteries and / or veins , spontaneous abortion, abnormally low number of platelets ( thrombocytopenia ), dotted purple skin (livedo reticularis), migraine headaches, a rare form of inflammation of nervous tissue of the brain and spinal cord and so on. The mechanism of fetal loss in pregnancy is not fully clear, but it is assumed that the reduced flow of Placental blood due to clots in the blood vessels of the placenta.
Multiple sclerosis can often be mixed up with Hughes syndrome. Symptoms that are common to Antiphospholipid syndrome and multiple sclerosis are: dizziness, problems with eyes, ataxia (drift when walking) loss of sensation, muscular weakness, difficulty in movement, problems with urination,fatigue, depression, difficult speech and so on. Symptoms that are characteristic only for Antiphospholipid syndrome include:thrombosis, migraine headaches, heart attack loss of memory, red rash in the form of seals, cramps, bruises, dry eyes, etc. Tests which are used for diagnosing of Hughes syndrome looking for molecules of phospholipids in the patients blood. They usually include: a test on anticardiolipin antibodies, test on lupus anticoagulant and VDRL / RPR (test for syphilis , which can be falsely positive in these patients).
But, antiphospholipid antibodies can also be found in healthy people due to infections by bacteria , viruses or parasites . Some medications can also affect their appearance in the blood, such as antibiotics, cocaine, hidralazin, prokainamid and quinine.
Treatment of each person with the Hughes syndrome demand individually approach in accordance with existing symptoms. Given that a large number of symptoms are associated with an abnormal grouping of platelets, treatment aims preventing blood clots by its dilution In the treatment of this disease uses anticoagulants (drugs that diluted blood) such as warfarin, coumarin or heparin with low molecular weight. Aspirin also affects platelets preventing their aggregation. Besides that, treatment uses cortisone drugs such as Prednisone.intravenous gamma globulin therapy is also applied to group of patients in wish were recorded spontaneous abortion and patients with low platelet counts during pregnancy.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...