
Lupus is an umbrella term used to describe diseases caused by the same underlying autoimmune disorder. In all autoimmune diseases, the body’s immune system attacks the body parts and organs, causing health problems and complications. Lupus can affect the skin, joints, blood cells and internal organs. Systemic lupus erythematosus is the most serious and the most dangerous kind of lupus. Lupus affects women more than men, usually between ages 10 and 50.
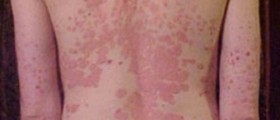
Lupus rash is a skin disorder resulting from lupus. This symptom is seen in as much as 90% of lupus patients. The symptoms and the severity of the rash vary from person to person but in all patients they are triggered by exposure to sunlight.
Causes and symptoms of lupus rash
It is not yet definitely known what exactly is causing lupus rash. In some patients genetics play a role, but there are still those who have no genetic predisposition to lupus rash. It is possible that the combination of hereditary and environmental factors contribute to the onset of lupus rash.
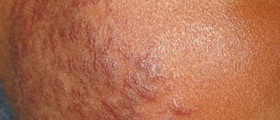
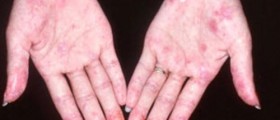
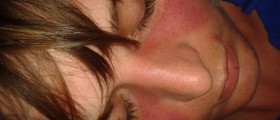
Lupus rash is the early sign of systemic lupus and discoid lupus. Discoid lupus affects large portions of the skin, causing hyper-pigmentation, scaling, flaking and crusting of the skin. Although it can occur anywhere, lupus rash is usually seen on the face, neck, shoulders and scalp. Lupus can cause consistent redness of cheeks, which is called malar blush. Skin affected with lupus usually becomes red, patchy, with lesions and nodules. It can be itchy or painful. Lupus rash on scalp can cause temporary or permanent hair loss.
Treatment for lupus rash
Lupus is a chronic disease so its manifestations, including the rash, can reoccur in regular intervals. In some patients the rash is constant and very difficult to treat. Unfortunately, there is no definitive cure for lupus or the lupus rash. There are, however, treatment options that can alleviate the rash and reduce its symptoms.
Treatment can consist of topical ointments based on steroids. Hydrocortisone is used for mild cases of lupus rash, while more severe cases require stronger medication, like betamethasone. Topical treatment for lupus rash is best and most effective if used in early stages.
Oral medications can be used to control the onset of the rash. Doctors generally prescribe antimalarial, slow-acting drugs that should be taken over an extended period of time.
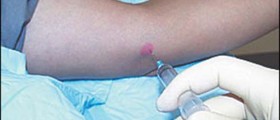
Painful lesions and discoid lupus rash can be treated with steroid injections. Because of their side effects, these long lasting shots are usually the last resort, when topical steroids help to alleviate the symptoms.










Your thoughts on this
Loading...