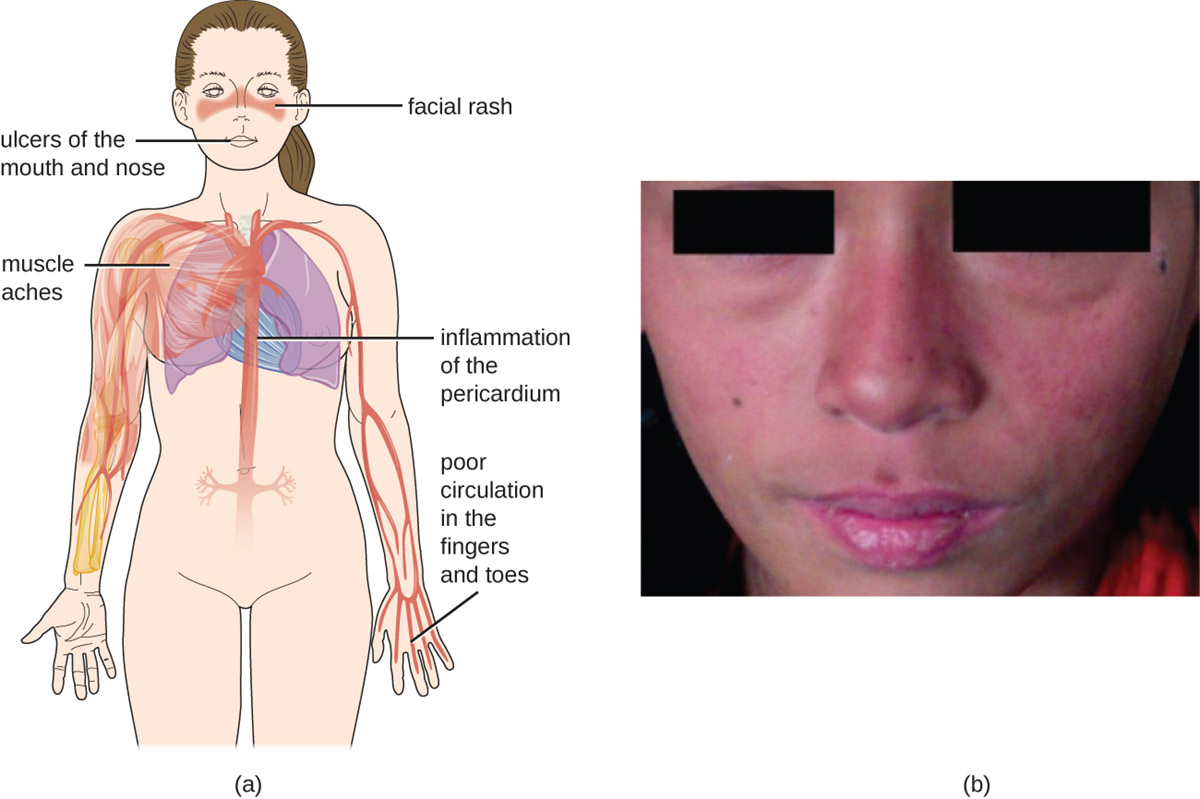
Chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus is a chronic skin condition. It is also known under the name discoid lupus erythematosus and is definitely one of the most common of all primary cicatricial alopecia. The condition predominantly affects women and is more common in adults than in children. The actual cause of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus has not been identified yet. Scientists believe there are many factors that can contribute to the disease and genetics and environment factors are only some of them. In some patients exposure to the sun represents a trigger for the disease.
In majority of cases the condition develops between the age of 20 and 40 and it is estimated that chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus in around 5-10% of adult patients progress into more severe form called systemic lupus erythematosus.
Clinical Characteristics of Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
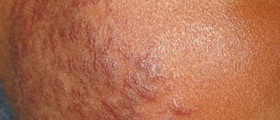
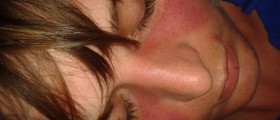
The condition can be further classified into several types including generalized discoid lupus erythematosus, lupus panniculitis and lupus tumidus. The names of these types are associated with specific changes that affect the skin. For example, in case of discoid lupus erythematosus skin lesions develop in a form of coin-shaped and scarred coin-shaped lesion. These skin lesions resemble a disc hence the name.
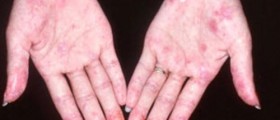
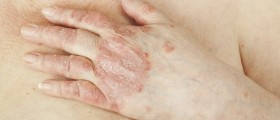
The skin lesions may differ among patients. They occur in a form of typical erythematosus, hardened and hyperkeratotic/thickened plaques or a person develops patches that seem not to be inflamed. In case of the last mentioned the process of inflammation actually exists but it is located deeper in the skin. It can be only confirmed with biopsy. If the condition affects the scalp, the lesions are erythematous and slightly elevated in a form of plaques or papules. Hyperkeratosis occurs in older lesions. Some of lesions are solitary while others merge together. Healing of lesions leads to scar formation and changes in color of the skin. The condition typically leads to increased shedding of hair, pruritus and stinging/burning sensation.
Treatment for Chronic Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus
It is necessary for the condition to be pathohistologically confirmed prior to starting with any treatment. Treatment for chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus is generally aggressive. Only this way permanent skin scarring as well as scarring alopecia can be successfully prevented. Early lesions respond best to the treatment.
In case of limited disease patients are administered class I or class II corticosteroids. They are applied topically. The same effectiveness is achieved with intralesional topical steroids. In case the initial treatment fails within a period of 8 weeks doctors prescribe anti malarial drugs. These medications are highly effective in case of chronic cutaneous lupus erythematosus. Positive results are noticeable within 4-8 weeks. There are several more therapies including retinoids, dapsone and thalidomide (the drug has only been experimentally administered to the selected number of patients). If the disease has significantly progressed patients can benefit from different surgeries such as excision, scalp reduction, hair transplantation and grafting.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...