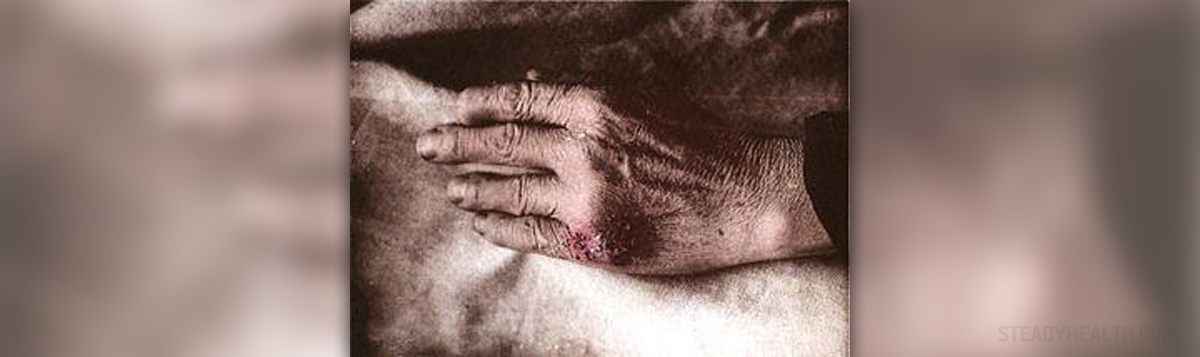
Lupus is a lon0-term autoimmune disease that can impact different tissues of the body, and cause them to become inflamed. When we say a disease is an autoimmune disease, it means that the human body itself starts attack its own health tissue after it produces antibodies to its own tissue.
The same thing happens to people diagnosed with lupus, and in these patients their own immune system creates abnormal antibodies which target a variety of tissues in the body. Because lupus can have many different symptoms, depending on which parts of the body are attacked by it, each patient is very much unique.
What Body Systems Can Lupus Affect?
Since the human body possesses antibodies and inflammatory cells in all its parts, this means lupus can affect any tissue or area of the organism. Lupus can provoke skin disease, but, for instance, certain heart, joint, nervous system, kidney or lung problems. Even the blood can be affected by lupus. Lupus may also be isolated only on the skin, without any internal disease. This type of lupus is known as discoid lupus, while the disease which affects any of the patient's internal organs is usually called systemic lupus erythematosus or SLE.
Lupus is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental issues, which means it can also run in families. Some types of lupus are induced by medications, such as certain high blood pressure drugs.
Lupus: What Are The Treatment Options?
SLE can’t be permanently cured, so the primary goal of treatment is to help the patient by easing the symptoms of the disease and decreasing autoimmune activity and inflammation in the body. In general, mild lupus symptoms don’t require any medical treatment or only some occasional anti-inflammatory drugs. However, serious cases of this disease could be associated with organ damage and have to be treated, usually with corticosteroid drugs and immune suppressants.
For mild cases of lupus, doctors usually recommend NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs), such as ibuprofen (Motrin), Aspirin, sulindac (Clinoril) or naproxen (Naprosyn). Which drug will be the best for an individual patient depends on the patient, and doctors may try several medications in order to define the one which best suits specific person. These medications may provoke unwanted side effects, like stomach discomfort and pain, ulcers, or even bleeding in some cases. Because of that, they are often recommended to be taken with some food or combined with drugs such as misoprostol (Cytotec), to protect the stomach and prevent ulcers.
Treatments for More Serious Cases Of Lupus
Corticosteroids, immunosuppressive drugs, certain anti-malarial medications, mycophenolate mofetil, certain antibodies and procedures like plasmapheresis, dialysis, surgeries or kidney transplant are also found to be helpful in more serious cases of lupus.
Corticosteroid drugs are more potent than NSAIDs and they are used in the treatment of SLE. High doses of these drugs taken over a long period of time could, however, also cause side effects such as weight gain, infections, diabetes, cataract, thinning of the bones and skin, as well as necrosis or the tissue in large joints. Immunosuppressive drugs (cytotoxic drugs) are also used for severe SLE cases, with some damage to internal organs. Doctors could prescribe methotrexate, azathioprine, chlorambucil, cyclophosphamide or Cyclosporine.
Anti-malarial medications like hydroxyxhloroquine (Plaquenil), chloroquine (aralen) and quinacrine may also be your doctor’s choice, especially if you have SLE which affects the skin and joints and causes severe fatigue. Mycophenolate mofetil (Cellcept) has been found to be efficient for patients with lupus that caused kidney (renal) disease, while antibodies like rituximab (Rituxan) and belimumab (Benlysta) may be useful to suppress B lymphocytes.
Plasmapheresis is actually a process where the blood is removed from the body, treated, and then returned to the organism, in order to remove abnormal antibodies. Some patients may need surgical removal of the spleen over the course of lupus treatment. Severe forms of SLE associated with kidney damage require dialysis and/or kidney transplant.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...