
Lupus in some people causes only mild symptoms but since the disease is chronic it may increase in severity. Lupus cannot be cured but there are treatment options to control symptoms and prevent severe damage to the organs. There are different types of lupus, namely discoid or cutaneous lupus, drug-induced lupus, neonatal lupus, subacute cutaneous lupus and systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE). Systemic lupus erythematosus is the most common and most severe form of lupus.
Causes of Lupus
Lupus and other autoimmune diseases develop due to unknown causes. Scientists believe that lupus in some people occurs due to genetic predisposition. External factors such as sunlight and viral infections may trigger the disease.
Symptoms of Lupus
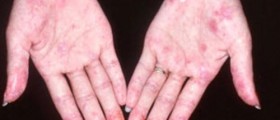
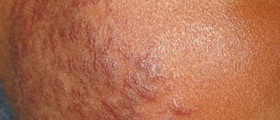
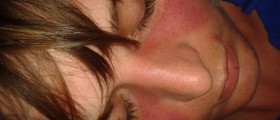
Symptoms of lupus greatly vary from person to person. Also, the symptoms may come and go. Lupus commonly causes feeling of tiredness and fatigue, pain in joints, muscle pain, swelling and low-grade fever. Skin rash may develop after exposure to sun. Some individuals may suffer from arthritis due to lupus.
Lupus can be also accompanied by mouth sores and hair loss. The disease may cause kidney inflammation, heart problems, lung problems, headache, seizures, vision problems, personality changes etc.
Diagnosis of Lupus
Lupus cannot be diagnosed with a single test. As symptoms can be variable, lupus can be hard to diagnose. On the other hand, in patients who have common symptoms of lupus and antinuclear antibodies (ANAs) in the body, lupus is diagnosed without difficulty. Still, ANAs can be present in the blood due to other conditions as well thus, additional testing is required.
Treatment for Lupus
Lupus can be controlled with the following medicines:
Topical corticosteroids for skin rash Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for fever and mild pain in joints and muscles Antimalarial drugs for fatigue, joint pain, skin rash and lung inflammation Oral corticosteroids given to control various symptoms that do not respond to other medicinesPrevention of Lupus
Systemic lupus erythematosus cannot be prevented. Since people who smoke have increased risk of lupus, avoiding use of different tobacco products may help to lower the risk of developing the disease.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...