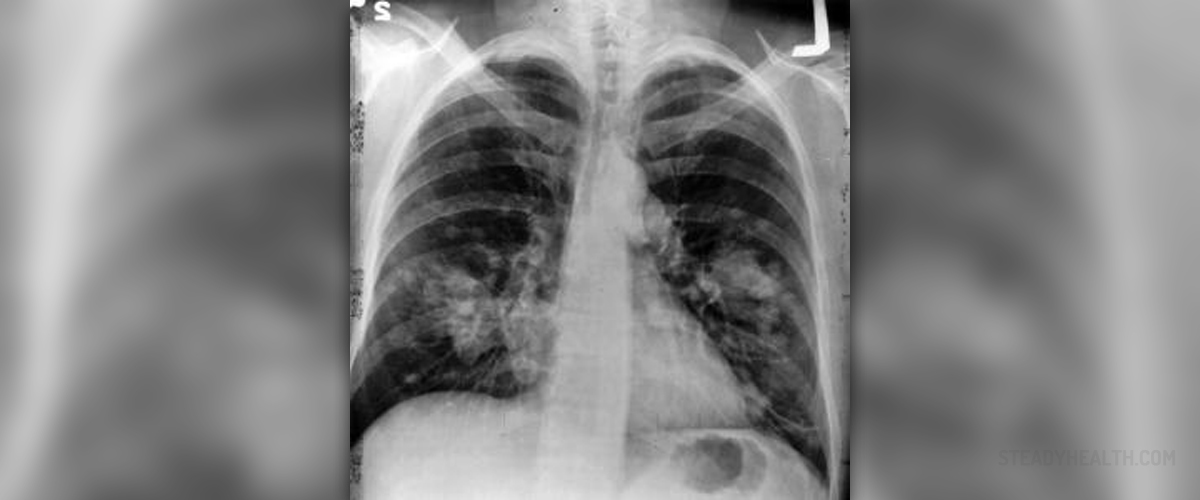
There are many infective illnesses of the lungs. Some of them are acute and successfully treated with suitable medications. Some lung infections may become recurrent and simply cannot be eradicated for good. There are several lung illnesses which are able to become chronic and they include tuberculosis, chronic bronchitis, emphysema, bronchiectasis and cystic fibrosis. The mutual characteristics of all chronic lung diseases which are associated with chronic infection is that they cause serious problems such as breathing difficulties and require prolonged if not permanent treatment.
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis is a serious lung infection. It can be successfully treated in initial stages. On the other hand, tuberculosis carries certain risk of becoming chronic. Tuberculosis predominantly affects the lungs although the infective agent may spread to other organs as well and cause additional problems. If tuberculosis becomes chronic it destroys lung tissue. The structure of the lungs is severely damaged which leads to serious breathing difficulties. The healthy lung tissue is replaced with specific formations called granulomas. The bacteria may enter the blood stream and spread to bones, kidneys and other organs causing even more serious symptoms and signs of the infection.
Chronic Bronchitis and Emphysema
Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are classified as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. In chronic bronchitis a patient suffers from chronic inflammation of the lung tissue. In emphysema the lungs are seriously damaged. There is an evident loss of alveoli which reduces the surface necessary for proper exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide. People suffering from emphysema are prone to infections and lung infection in this case occurs in a chronic form. Both of the mentioned conditions, chronic bronchitis and emphysema are associated with heavy smoking and exposure to industrial and environmental irritants.
Bronchiectasis
Bronchiectasis is a medical condition which features with irreversible dilation of certain parts of the bronchia tree. Affected bronchi are dilated and inflamed, filled with secretions and are prone to recurrent infection. People suffering from bronchiectasis have to deal with frequent lung infections.
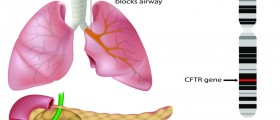
Cystic Fibrosis
Cystic fibrosis is another lung condition associated with frequent lung infection. The symptoms (shortness of breath, cough etc) in this case develop as a consequence of accumulation of thick, sticky mucus which simply cannot be expelled. The very presence of mucus in the airways makes a person highly susceptible to recurrent infections. Cystic fibrosis requires prolonged treatment with antibiotics and occasional change of administered antibiotics since bacteria may become resistant if one antibiotic is used for a longer period of time.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia may be acute or chronic. Chronic pneumonia predominantly affects immunocompromised patients (those suffering from cancer, HIV/AIDS etc). These patients are susceptible to infection since their immune system does not function properly and severe from of lung infection can be caused by many infective agents such as fungi, bacteria and viruses.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...