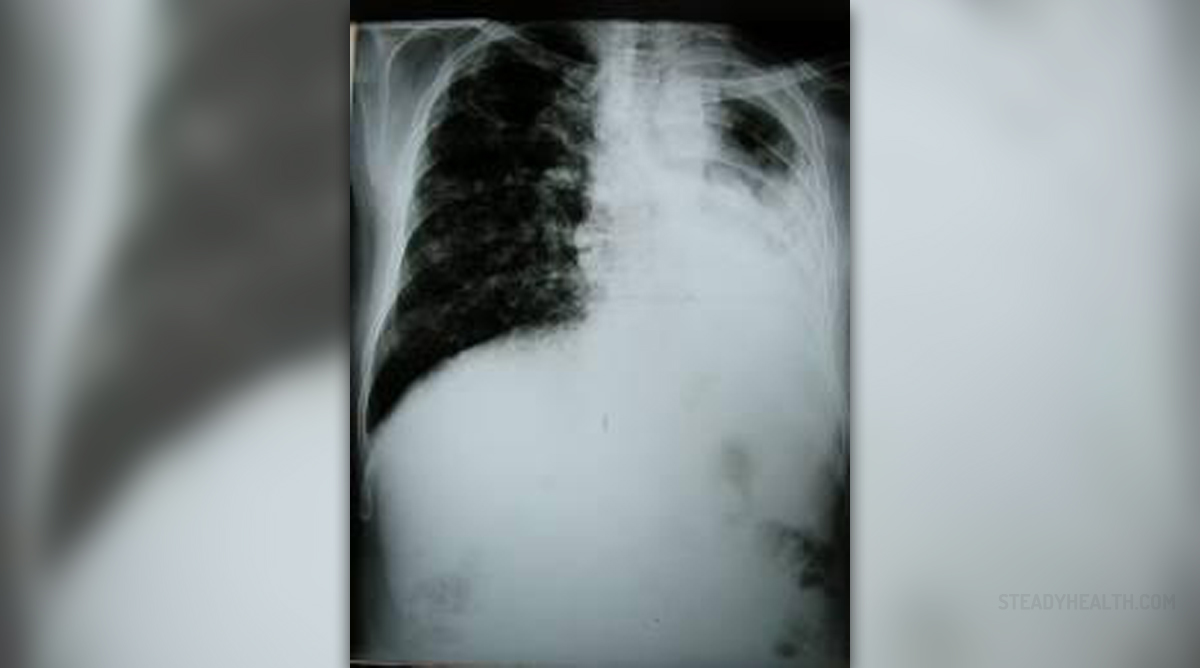
General Info about Tuberculosis
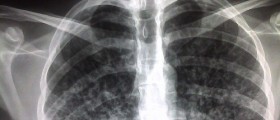
Tuberculosis is a serious and deadly contagious disease. The infection is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the infective agents are spread through the air. The most common way of transmission is coughing, sneezing and close contact with the infected person. Even though the lungs are the primary site of the infection tuberculosis may also affect other organs such as the lymphatic system, central nervous system, circulatory system, genitourinary system, bones, joints and skin.
If left untreated tuberculosis is highly lethal. Until the scientist have found antibiotics the infection had led to death of millions of people around the world. Today it is treated successfully although the treatment includes several antibiotics and lasts for several months.
Current Treatments for Tuberculosis
It is essential to follow certain rules in order to eradicate the disease. Treatment for tuberculosis is rather complex and it takes some time for all the bacteria to be eradicated.
The treatment for tuberculosis includes several medications. There is a need for multiple medications since the bacteria can be resistant to one antibiotic and it can be more susceptible to other antibiotics. Furthermore, patients must stick to prescribed regimes. The drugs must be taken on time. This maintains optimal concentration of the drugs in the blood and helps in eradication of infective agents. Since the bacteria responsible for tuberculosis may be stubborn the treatment generally lasts for several months.
Majority of patients eventually get cured. The current treatments for tuberculosis include several antibiotics, isoniazid, rifampin, ethambutol and pyrazinamide. They are used in different combination.
Isoniazid is one of the most powerful medications against Mycobacterium tuberculosis. It is not expensive and is easy to take. The best results are achieved if isoniazid is combined with other antituberculous drugs.
In some cases people are administered medications to prevent the onset of the infection. Namely, people who have been in a close contact with the infected person, those with positive tuberculin skin test reaction, people with abnormal chest X-ray that points to inactive tuberculosis, people whose tuberculin skin test changed from negative to positive within the past 2 years as well as those with positive skin test reaction and a special medical condition (immunocompromised patients) require preventive intake of antituberculous medications.
Apart from isoniazide rifampin is another antituberculous medication of great potential against Mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Even in case some strains show resistance to isoniazide the drug is still taken since there is a chance for some microorganisms to be sensitive to the drug. This is why there is a need to drugs to be combined. A combination of drugs is much more efficient in battle against resistant microorganisms.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...