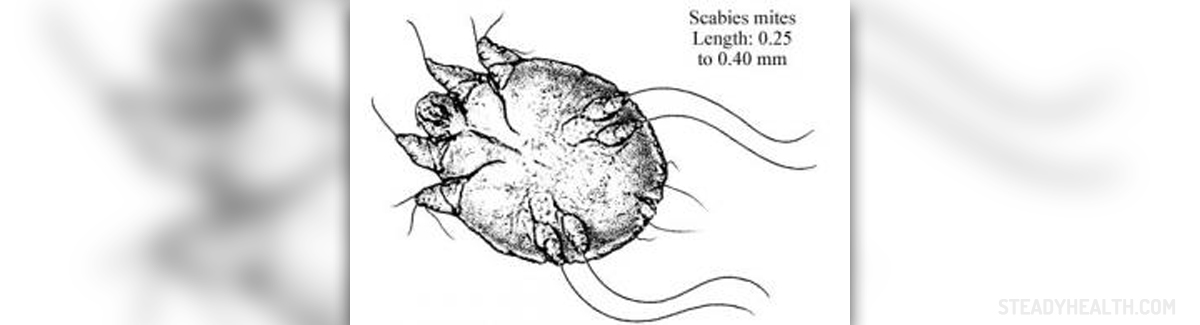
Scabies
Scabies is a rather common skin infection and is caused by ectoparasite called Sarcoptes scabei. This parasite has 8 legs, is approximately 0.3 inches long and what has been definitely proved is that only female Sarcoptes scabei causes infection in humans. Parasites cannot be noticed by naked eye, only with the assistance of microscope. Sarcoptes scabei cannot survive outside the host's body. On the other hand, once the infection has occurred parasites may live up to a month. The disease affects people all over the world. However, it is most frequent among poor and homeless people.
Symptoms of Scabies
In those who have never been exposed to scabies before, the symptoms occur approximately 4 to 6 weeks after infestation. Parasites dig superficial burrows and this causes intensive itching, generalized rash and potential secondary infection. In infants the disease may feature with blisters and pustules on the hands and feet. Skin changes may be in a form of S-shaped tracks formed by tiny nodules. These skin changes resemble pimples and typically affect crevices of the body. The rash and itching are consequence of body's immune reaction to the presence of scabies mites. In immunocompromized people the rash caused by scabies may spread and affect large portions of skin. Majority of patients report intensive itchiness during night. Skin changes are susceptible to secondary bacterial infection especially if scratched. This can cause impetigo or even celulitis.
Is Scabies Contagious
Scabies is highly contagious and easily spread among people. Even hugging can cause spread of mites. This normally does not include quick hug but one that is typical for mothers and their babies and similar types. This only points to the fact that adult parasites can be transferred even more easily. Apart from direct spread of parasites, the disease can be also transmitted by sharing of infested clothes, towels, and bedding.
Sexual contact is another way of passing the infection. This is only one more way of spreading of the disease and the reason why scabies cannot be simply classified as sexually transmitted diseases.
The basic problem related to contagiousness is that people who have been exposed to parasites may not develop symptoms of the disease during incubation. This does not mean they are healthy. On contrary, even during incubation people are infective and parasites can be easily spread.
Fortunately, after the onset of treatment parasites keep on being contagious for about 10 hours and then they are no longer threat to nearby healthy people. Parasites which remain on clothes, bedding etc. may survive up to 4 days and unless they found new host they eventually die.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...