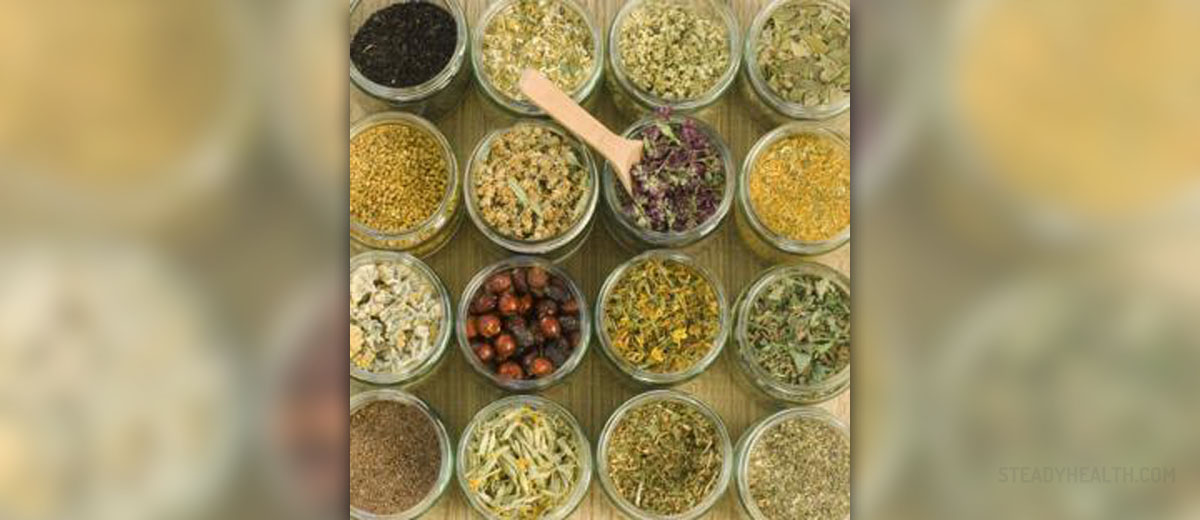

Herbalism is a traditional folk medicine, or the traditional medicinal practice, based on the use of plants and plant extracts found in the nature. This discipline is also known as botanical medicine, medical herbalism, herbal medicine, herbology and phytotherapy. Many compounds used today in the modern mainstream medicine are actually derived from various plant sources. Most of these medicines are even used in a very similar way as their herbal correlatives. Medical herbalism greatly evolved during many centuries, and today it represents a highly sophisticated system of natural medicine that is able to treat various physical and mental disorders, often without any side effects.
The history of herbalism
Herbal remedies are the first medicines humans ever used. There is strong evidence that even Neanderthal men used herbs and pollen from different plant species, to cure diseases. The ancient Sumerians left the written record of herbalist practice, as well as the Egyptians, who used garlic, opium, castor oil, coriander, mint, indigo, and other herbs for medicine, back in the 1000 BC. Herbalism was also popular in China, and the first book on herbalism was compiled during Han Dynasty, in 2700 BC. The herbalist practice of ancient Greeks and Romans was preserved in the writings of Hippocrates and Galen. These writings were copied later in the early medieval European monasteries, which became real centers of medical knowledge, and from which the first modern medical schools developed.
The theory of herbalism
According to the theory of herbalism, certain herbs possess actual medicinal value and can be beneficial to human health. Some of the herbs can alleviate the symptoms of various diseases, or even cure them, while the others help to prevent different ailments. All herbs produce different chemical compounds, as part of their normal metabolic activity. Some of these compounds are not essential for basic vital functions of the plant, and they are often found only in particular genus or species. The functions of these secondary metabolites are different: sometimes they are toxins used to deter a predator, or pheromones used to attract insects. However, the chemical profile of each plant determines its medical potential and use by humans.
Unlike the conventional medicine, herbal practitioners use whole herbs, without breaking it down in chemical compounds. Herbalists believe that a plant represents an ideal, naturally established, balance of beneficial elements that work together to improve human’s health. Even when the herbalist makes herbal extracts from leaves, roots or other parts of the plant, the principle remains the same. The secondary metabolites and pigments from plants possess therapeutic properties and, according to the herbalism, they should be used integrally without altering their natural properties.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...