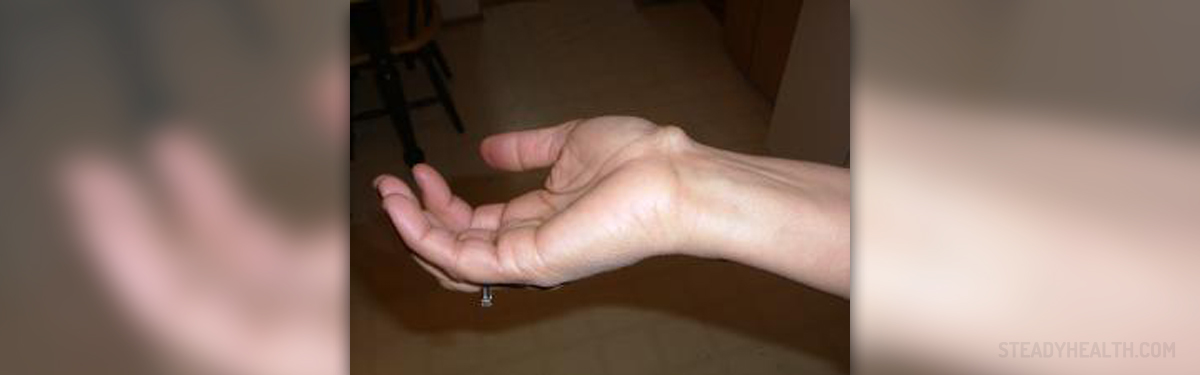
A ganglion cyst is a sort of lump that forms near a joint or a tendon. These cysts are do not lead to serious medical complications, since they are benign growths filled with fluid. Moreover, they are not infectious and they do not tend to expand to the other parts of the body.
Despite the fact that ganglion cysts may be formed next to any joint in our body, in most cases, they appear in the wrist. A dorsal ganglion cyst is a ganglion cyst that emerges on the top of a wrist. However, ganglion cysts may also be seen on the underside of the wrist, for example, in the area from the pulse point to the thumb, or at the base of any finger.
The first warning sign of a ganglion cyst near the wrist is swelling in that area. Although ganglion cysts are not cancerous, they tend to grow in size over time. The ganglion cyst forms on the fibrous tissues between the muscles and bones and the fluid in them is similar in nature to the fluid found in the joints (synovial fluid). When ganglion cysts grow in size, they place a significant amount of pressure on the surrounding nerves, thus causing pain. If a person with a wrist ganglion cyst does not rest the affected area and uses or moves the affected wrist more than minimally, the ganglion cyst tends to grow.
Causes of wrist ganglion cysts
Even though the chief cause of the occurrence of ganglion cysts in the wrist is not discovered yet, it has been noticed that this condition affects women more frequently than men, and particularly those from 20 to 40 years of age. a constant pressure to the wrist and overuse of computers are some of the possible causes for the incidence of wrist ganglion cysts.
Treatment of wrist ganglion cysts
First of all, the doctor must diagnose the presence and the type of ganglion cyst in order to give the appropriate treatment to the patient. In the majority of cases, ganglion cysts tend to resolve on their own without any specific medical treatment. However, there are also ganglion cysts that grow in size over time.
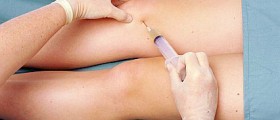
One of the treatments of wrist ganglion cysts includes the immobilization of the wrist. Thus, the pressure on the nerve is reduced and the ganglion cysts may disappear. The fluid from the ganglion cysts can be also removed by means of a needle inserted into the cyst's sac, through which the fluid is aspirated (drained out). As the sac itself remains intact in this case, it is possible that the cyst will come back in time. That is why patients should know that wrist ganglion cysts may also be removed by means a surgery carried out under local anesthesia, in which case the whole cyst is removed intact, including the sac. Once the ganglion cysts are removed, there is still a possibility that they may recur over time, however, you will find comfort in knowing that the same cyst will not be able to simply fill with fluids again.








-Arthritis_f_280x120.jpg)

-Symptoms,-Diagnosis,-Treatment_f_280x120.jpg)

Your thoughts on this
Loading...