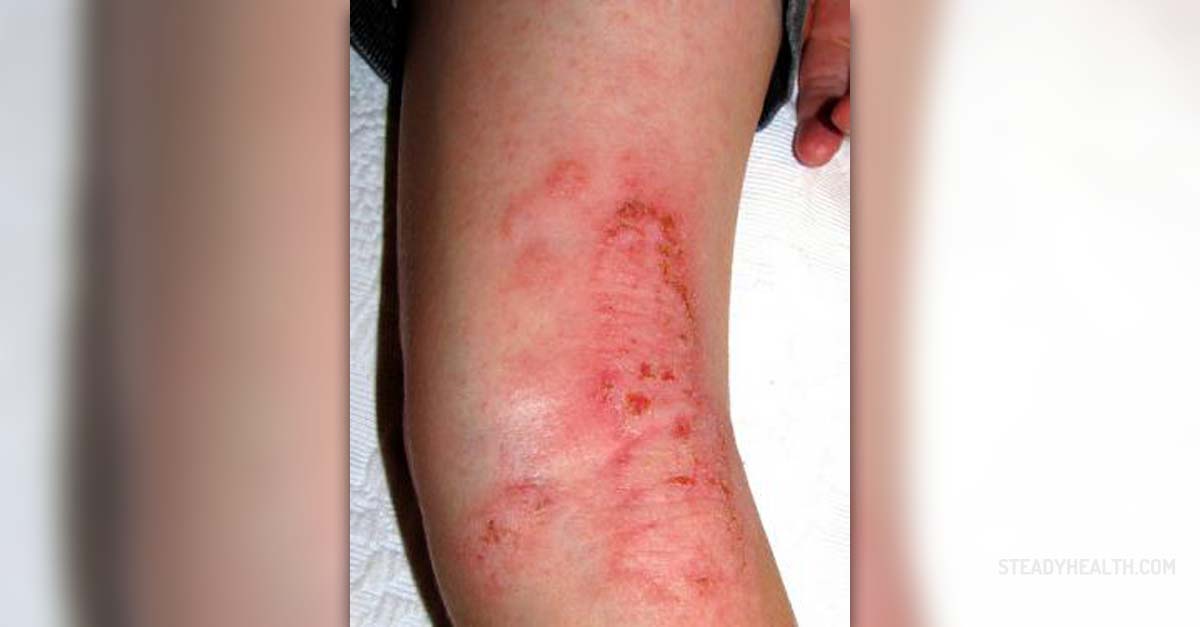
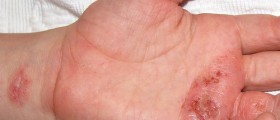
Atopic eczema is one of several types of eczema that affects the skin. The condition is characterized by red, itchy and scaly rash. The affected area may also be covered with oozing blisters and the surrounding skin is usually red or of a color different than normal due to frequent scratching. In case of atopic eczema people are highly susceptible to certain allergens which actually trigger the condition. Different foods are only some of potential triggers for atopic eczema.
Atopic eczema is commonly associated with different allergic conditions such as allergic rhinitis, asthma and other respiratory allergies. The condition is genetic and patients who develop atopic eczema are actual members of families with history of different allergic conditions (asthma, hay fever, eczema etc.).
Eczema and Food Allergies
It is estimated that approximately one third of all patients suffering from eczema actually develop an allergic reaction when exposed to certain food products. Allergens found in different food products may cause worsening of the already existing eczema or induce flare-ups. This is why avoiding certain foods that may trigger the condition can effectively eliminate symptoms. Some of the most common food triggers of eczema are eggs, milk, peanuts, soy and wheat. The eggs in majority of cases represent the culprit of specific skin changes. Due to the previously mentioned in patients suffering from eczema it is essential not only to perform standard allergy testing but to search for all potential food allergens that may induce the symptoms and after they have been identified to eliminate them from the patient's diet.
Non-Food Eczema Triggers
Apart from food allergens eczema may be triggered by stress, physical irritants, airborne allergens and some infections. Tobacco smoke, certain chemicals (soaps, shampoos, washing powders etc.), paints etc. are several examples of irritants associated with eczema. Furthermore, harsh weather conditions are also potential non-food triggers of eczema. The condition also occurs due to an allergic reaction to pollen, dust mites, feathers, mold, pet hair etc.
Treatment for Eczema
In order to prevent the occurrence of symptoms patients suffering from eczema should stay away from potential allergens (avoid triggers of eczema). Foods that contain allergens must be completely eliminated from one's diet. If inflammation occurs it is brought under control with anti-inflammatory drugs such as topical corticosteroids.
Some studies have shown that in children with positive family history of eczema the onset of eczema may be prevented with breastfeeding and late introduction of solid foods. Some studies are even investigating the effects of probiotic supplements but the results are still inconclusive.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...