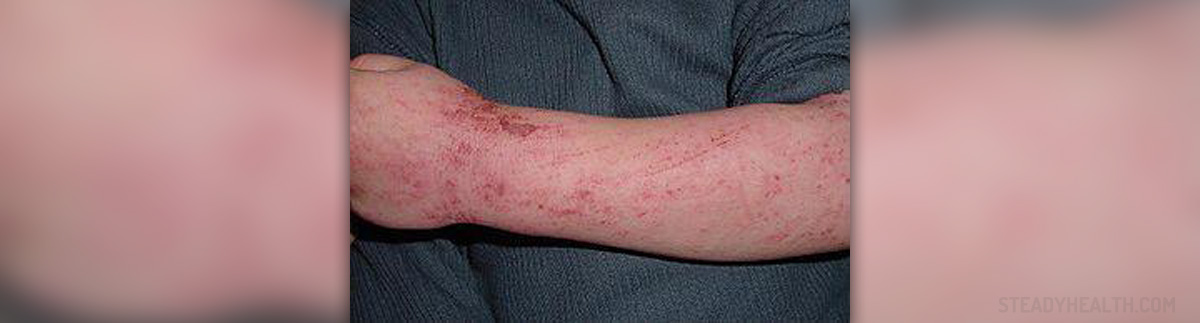
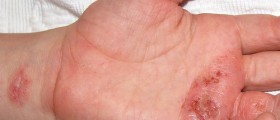
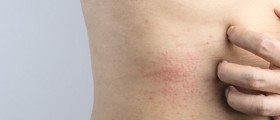
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin disorder that cannot be transmitted from one person to another and is almost always accompanied by pruritus.
Atopic Dermatitis - Overview
In people suffering from atopic dermatitis the skin reacts inadequately once an individual is exposed to some irritants, food or environmental allergens. The affected skin becomes red, flaky and quite itchy. Additionally, the skin becomes more susceptible to infections (especially bacterial infections). In the majority of patients the inflammation is located on the flexural surfaces of the joints. The hands and feet, ankles, wrists, face, neck and upper chest are also common predilection places of skin inflammation.
People afflicted with atopic dermatitis are also prone to other atopic illnesses such as asthma or hay fever. Even though there is no cure for atopic dermatitis, the condition is easily treated and symptoms and signs of skin inflammation soon subside. Moreover, with adequate preventive measures recurrence of the condition is generally postponed for a long period of time.
Atopic Dermatitis Treatment Options
With suitable treatment symptoms and signs of atopic dermatitis may completely vanish within 3 weeks. In many cases such desirable effect is achieved with the combination of corticosteroid medications and moisturizers. In order to receive the best possible treatment, patients are due to consult a well experienced dermatologist who will make an individual treatment plan.
Firstly, people suffering from atopic dermatitis should prevent skin dryness. Bathing long with frequent application of moisturizers may keep the skin well hydrated and moist. One should always use lukewarm water and avoid harsh gels, soaps and bath oils. For the best effects moisturizers should be applied immediately after taking a bath.
Secondly, patients are due to avoid irritants that initiate skin inflammation or make the already existing inflammation worse. Apart from avoiding irritants, one is due to stay alway from allergens which may come in direct contact or are inhaled or ingested.
Finally, even though the skin is very itchy, one should not scratch it especially if the fingernails are long and sharp.
Atopic Dermatitis Medications
As it has been mentioned, topical corticosteroids (creams/ointments) may successfully reduce skin inflammation.
Calcineurin inhibitors represent a group of topical immunosuppressive agents. Because these drugs may induce cancer, their administration is limited to cases of atopic dermatitis that do not respond to other treatments.
Antihistamines are highly efficient against itching and antibiotics, antifungal medications or some antiviral drugs are administered only if there is secondary infection caused by certain microorganisms.
Severe cases of atopic dermatitis may require additional treatments such as exposure to ultraviolet light, high-strength topical corticosteroids, Cyclosporine or interferon.












Your thoughts on this
Loading...