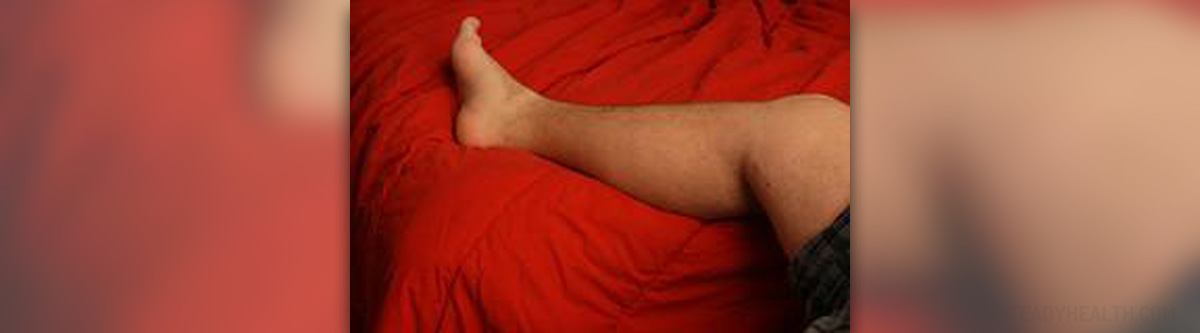
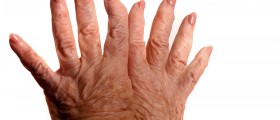
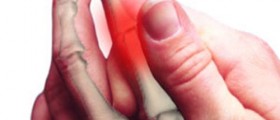
Complex regional pain syndrome is a chronic and progressivetype of disease which can is typically characterized by certain changes in theskin, swelling and unbearable painful sensations. There are two different types ofcomplex regional pain syndrome and the classification is based on the presenceor absence of nerve lesions after an injury. Complex regional pain syndrometype I is a medical condition without the aforementioned nerve lesions and itmay also sometimes be referred to as algoneurodystrophy, reflex neurovasculardystrophy, Sudeck’s atrophy or reflex sympathetic dystrophy. Complex regionalpain syndrome type II is associated with nerve lesions and nerve damage. Thereare no known causes of complex regional pain syndrome but certain factors such assurgeries and injuries may increase the risk of precipitation. Thesensitization of the central nervous system seems to be the key neurologicprocess in the induction and maintenance of complex regional pain syndrome.According to certain scientific studies, this process may be associated withelevated levels of CNS glutamate in affected persons. Other possible factorswhich may be connected with the syndrome includeoxidative damage, cortical reorganization, glial cell activation,adrenoreceptor pathology, sympathetic afferent coupling, exaggerated neurogenicinflammation and trauma related cytokine release. The most common symptoms ofcomplex regional pain syndrome usually occur near the site of the injury.In most cases they involve painful sensations, electrical sensations andburning sensations. Other less common symptoms which may be a part ofcomplex regional pain syndrome are painful movement, restricted movement,joint stiffness, joint tenderness, thinning of the bones, softening of thebones, changes in the skin color, changes in the skin temperature, abnormallyincreased sweating, local swelling and muscle spasms. It is a widely known factthat physical or emotional stress may aggravate the existing symptoms of complexregional pain syndrome. Duration and severity of the aforementioned symptoms mayvary, depending on the individual case. There are three different stages of complex regional pain syndrome. Patients in the first stage of the syndrome experiencesymptoms such as the vasospasm, rapid nail growth, rapid hair growth,restricted mobility, joint stiffness, muscle spasm and severe burning pain atthe site of the injury. The second stage is commonly accompanied by muscleatrophy, thickening of the joints, severe osteoporosis, spotty, grooved,brittle and cracked nails, diminished hair growth, swelling and intense painfulsensations. The third stage involves bone thinning, bone softening, flexortendon contractions, severely limited mobility of the affected area, muscleatrophy, irreversible changes in the skin and excruciating pain.
History and Nomenclature
The CRPS was first described by Silas Weir Mitchell and itwas given its name by his friend Robley Dunglison. The umbrella term complexregional pain syndrome was first coined in 1993 and it has been in use eversince.
Different Treatment Options
Among the most important components of different treatmentmethods for those who suffer from complex regional pain syndromethere are physical and occupational therapy. Some people have plenty of troublewith physical therapy simple due to the fact that they suffer from touchintolerance. Certain types of drugs are also commonly used in the treatment ofcomplex regional pain syndrome. These drugs include various different typesof opioids, alpha adrenergic blocking compounds, beta adrenergic blockingcompounds, GABA analogs, vasodilators, bisphosphonates, COX inhibitors,corticosteroids, anti inflammatory medicaments and antidepressants. Mirror boxtherapy may also be of great help when it comes to reducing the levels ofpainful sensations in those who suffer from the syndrome. Such treatment approach may additionally reduce the disability in certain acute cases of complexregional pain syndrome. Graded motor imagery may be highly efficient when itcomes to the reduction of disability and painful sensations in patients whosuffer from chronic cases of complex regional pain syndrome. Another successfulmethod of treatment is referred to as tactile discrimination training. It iscommonly used in cases of phantom limb pain. Among the already mentioned methods oftreatment there are injections of a local anesthetic such as lidocaine whichmay sometimes even be repeated. Some patients feel significant pain relief thanks to topicallidocaine patches. Some cases of complex regional pain syndrome may call forthe surgical implantation of the spinal cord stimulator. This type of device isintended for the reduction of pain induced by direct stimulation of the spinalcord. Interruption of the affected portion of the sympathetic nervous system isa process referred to as sympathectomy and it may be used in severe casesof complex regional pain syndrome, the ones that cannot be brought under control with any other treatment. Ketamine is one more drug which may be usedin patients suffering from complex regional pain syndrome. And finally, alternative treatment options include hypnosis, relaxation techniques andpsychotherapy.
Prognosis
Early treatment of complex regional pain syndrome may beassociated with a good prognosis. Bad prognosis is commonly connected to limb amputations.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...