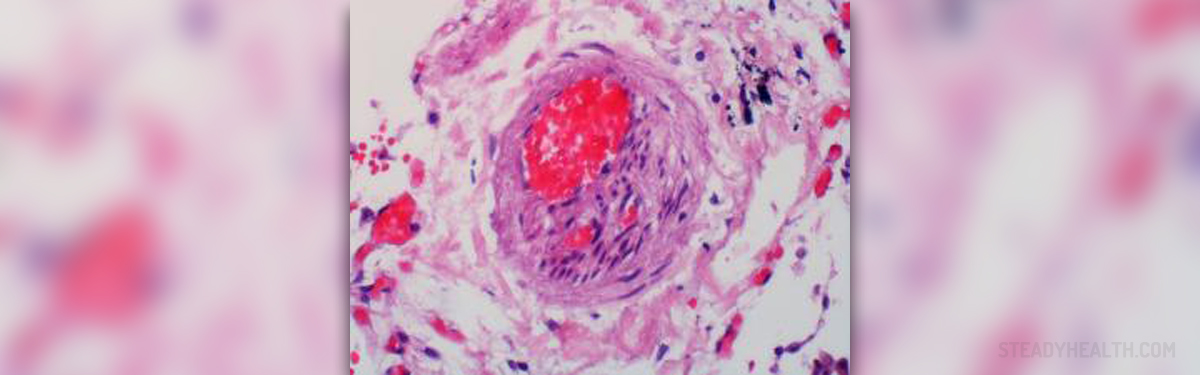
Deep vein thrombosis is a condition in which thrombus (a blood clot) forms inside one of deep veins. Deep veins in the legs are most commonly affected. The very presence of the thrombus may be asymptomatic or a person complains about pain in the affected area.
Deep vein thrombosis develops as a consequence of improper circulation and stasis in the veins. This is why it generally affects people who spend too much time sitting (such as those traveling to distant places by plane or car). Furthermore, deep vein thrombosis affects people who are already suffering from certain medical conditions associated with hypercoagulation.
There are some risk factors that contribute to deep vein thrombosis. Apart from spending too much time sitting the condition is also associated with prolonged bed rest (period after extensive surgeries or patients who are paralyzed), pregnancy, obesity, smoking, some types of cancer, heart failure, birth control pills, a history of pulmonary embolism and a family history of deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism.
What Are Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis?
It is estimated that in around half of patients deep vein thrombosis does not cause any symptoms or signs. However, if they occur, patients most commonly report swelling of the affected leg (particularly swelling of the ankle and foot), pain that generally starts in the calf and may be described as cramping and redness and/or warmth of the skin.
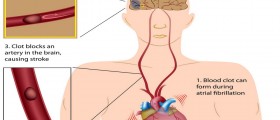
If left neglected deep vein thrombosis may further progress into pulmonary embolism. This complication occurs if the blood clot separates and travels to the lungs. Warning signs of pulmonary embolism are sudden shortness of breath, chest pain or discomfort, coughing up blood and feeling lightheaded or dizzy.
Treatment for Deep Vein Thrombosis
The goal of the treatment for deep vein thrombosis is a reduction of the blood clot and prevention of pulmonary embolism. There are several treatments available.
Blood thinners are drugs able to dissolve blood clot and they are usually administered in a form of a shot or infusion. Heparin is one of blood thinners used on patients suffering from deep vein thrombosis. Intravenous form of medication may be eventually replaced with a suitable oral drug. The actual length of anticoagulation therapy depends and may linger for several months.
Clotbusters are administered to patients with more severe form of the disease and those suffering from pulmonary embolism.
People who cannot take medications that prevent blood clotting are inserted a filter into a large vein called the vena cava. The vein is located in the abdomen and such filters catch blood clots and prevent their further flow to the lungs.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...