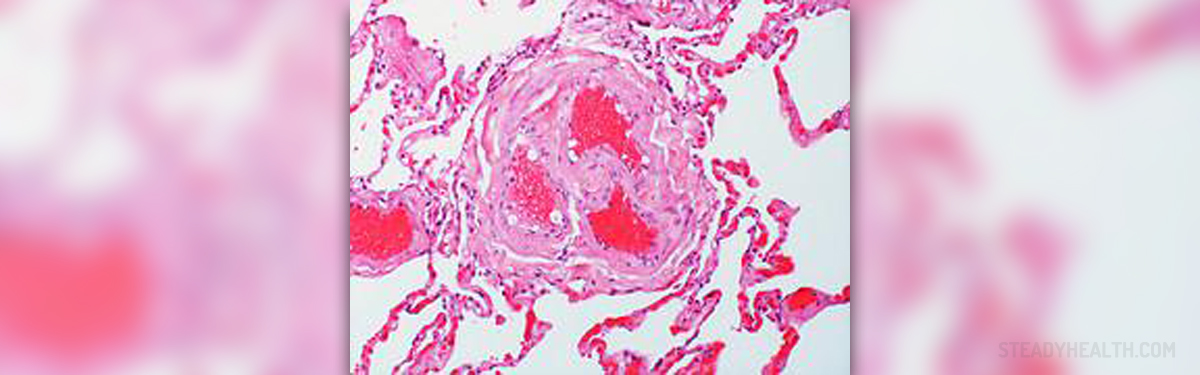
Formation of a blood clot (thrombus) in a deep vein is the condition called deep vein thrombosis (DVT). This usually occurs in the legs. Blood clots can develop in superficial veins as well. This condition is known as superficial thrombophlebitis or phlebitis and it is rarely associated with serious complications. On the other hand, deep vein thrombosis can cause permanent and life-threatening problems.
It is estimated that in the U.S. between 350,000 and 600,000 people get affected by deep vein thrombosis each year. The condition most commonly occurs in deep veins of the calf and thigh. Rarely, blood clots develop in the arms and pelvis.
Causes of Deep Vein ThrombosisBlood clots may develop due to immobility as it causes blood flow to be slow and susceptible to clotting. This is common in people who are confined to bed or are traveling long distances. Surgery (particularly of a hip or knee), trauma to the lower legs, obesity and pregnancy can also lead to formation of blood clots and deep vein thrombosis.
People with family history of blood clots have increased risk of deep vein thrombosis. Cancer and medications such as contraception pill and hormone replacement therapy also increase the risk of blood clot formation.
Symptoms of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Small blood clots usually do not cause symptoms but are identified when complications occur. However, larger clots are associated with obstructed blood flow in the vein which may cause pain and swelling in the affected leg, including the ankle and foot. Redness and warmth of the leg are also present.
Diagnosis of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis can be diagnosed using an ultrasound test which shows blood flow through the veins and any blockage to blood flow. A doctor may also use other diagnostic tests such as venogram which involves injecting dye into veins to detect a blood clot.
Treatment for Deep Vein Thrombosis
Deep vein thrombosis is commonly treated with anticoagulants or blood thinners used to prevent blood clots from getting bigger. Sometimes, thrombolytic medicines are used as well. Thrombolytics work by dissolving blood clots.
Prevention of Deep Vein Thrombosis
Preventive measures are required for any patient with increased risk of deep vein thrombosis. After any major surgery, particularly those performed on the leg, lower abdomen or hip the patient is given an anticoagulant medicine to lower the chance of blood clot formation.
People who are sitting too long should exercise their calf muscles to improve circulation in the legs. Patients who have been on bed rest should start moving as soon as possible to prevent formation of blood clots.
Compression stockings can also reduce the risk of deep vein thrombosis. Compression stockings should be worn when going on a long distance airplane travel. Finally, overweight people should lose weight to lower the risk of deep vein thrombosis.














Your thoughts on this
Loading...