Blood Clots - General Info
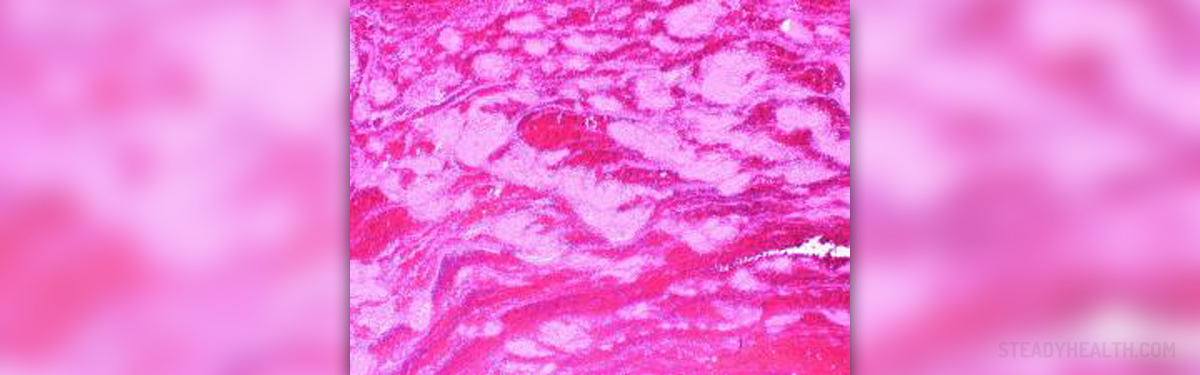
Blood clotting can be defined as a process during which the platelets, red blood cells and fibrin form a clump. The purpose of this clump is to stop bleeding caused by injury to blood vessels. In case this process occurs at the surface of the skin the wound is eventually covered with a scab which prevents further bleeding. However, blood clotting may also occur even if there is no damage to the blood vessels. Internal blood clotting takes place inside the blood vessels and is caused by many factors. The formation of clots in this case represents a serious risk factor since clots may break and travel down the blood stream and eventually lead to blockage of certain blood vessels.
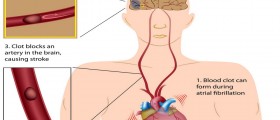
Deep vein thrombosis is a condition which features with formation of blood clots in deep veins of the legs. These blood clots may break, travel to lungs and cause life-threatening pulmonary embolism. These two medical conditions are responsible for lethal outcome of about 100.000 people in the United States each year.
Blood Clots after Surgery
Surgery increases risk of blood clotting even in patients who have never experienced any problems related to blood coagulation. This can be easily explained by the fact that surgery and any kind of injury stimulate blood clotting. In majority of patients blood clots after surgery form within 2 weeks after the surgery. However, they may occur even a few hours after the surgery.
There are certain types of surgical procedures and trauma which are associated with higher risk of blood clotting. They include pelvic surgery (gynecologic or urologic surgery), orthopedic surgery (hip replacement, fracture repair etc.), spinal cord paralysis, multiple fractures of extremities and finally, hip socket injury.
Prior every surgery patients are evaluated for any risk factors for blood clotting. There are several preventive measures which include administration of anticoagulants, special stockings or automated calf compression devices which may be applied in patients with increased risk of blood clotting. The best way is to perform rapid mobilization which means that patients are supposed to get out of bed as soon as possible. This way the blood will circulate better and the chance of blood clotting drastically decreases.
Symptoms of Blood Clots
The symptoms may be mild and sometimes resemble symptoms of other medical conditions. Deep vein thrombosis usually features with swelling and pain in the affected limb and skin redness. The skin is usually warm.
In case blood clot breaks and reaches the lungs pulmonary embolism develops. This condition features with breathing difficulties, chest pain and tightness, cough, rapid heart beat, fainting. There is also mild fever.















Your thoughts on this
Loading...