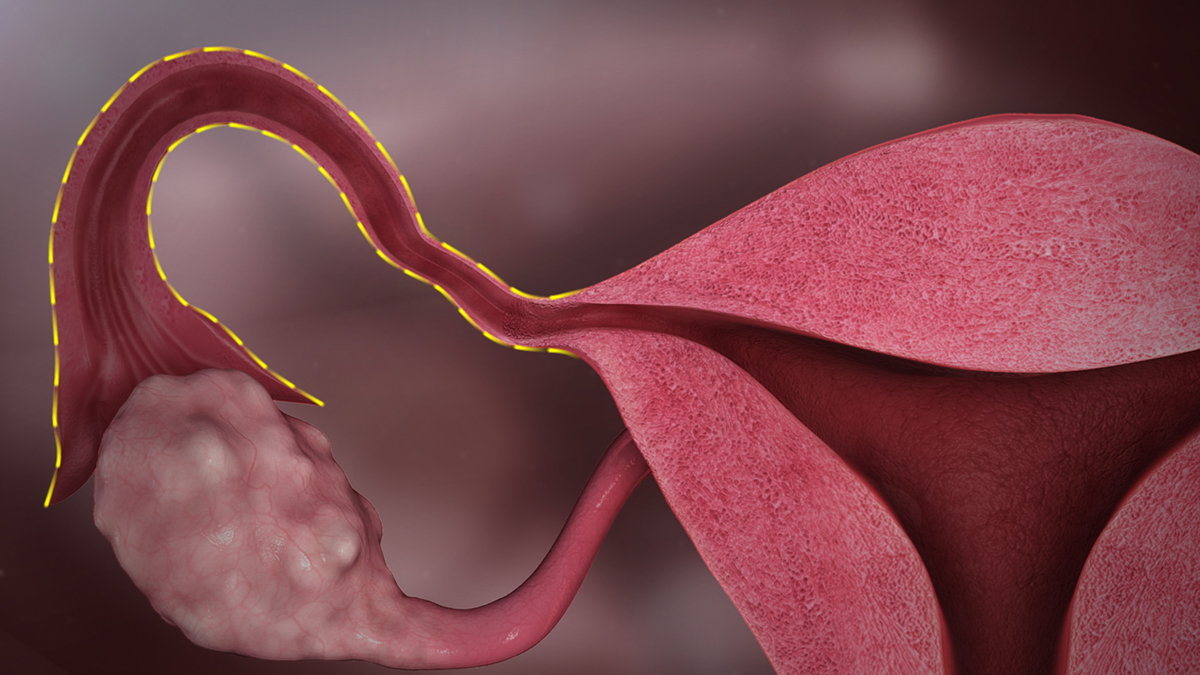
Complications with Fallopian Tubes
It is estimated that in the US fallopian tube damage accounts for up to 25 percent of all infertility cases in women. The causes of fallopian tube damage are usually unclear and it is often unknown when the damage first occurred. The signs and symptoms are similar to those of the PMS so most women are unaware there are any problems until they try to get pregnant. The most common symptoms are heavy menstrual bleeding and painful periods, but such occurrences can be present without any disorders in the fallopian tubes. Further, tubal damage is a broad term that encompasses various problems in the area. There can be layers of debris along the tube walls, which hinder the traveling of an egg and in turn reduce the chance of getting pregnant. Blocked tubes are also problematic as they make it difficult for the sperm to reach the egg. When it comes to the causes of fallopian tube damage in most cases the responsible agents are infections such as gonorrhea, chlamydia and pelvic infections. There are other instances in which infections from other body parts spread to the tubes. Lastly, surgery to the fallopian tubes can leave them damaged causing additional debris to deposit. In cases in which the primary health care provider or a gynecologist believes the patient might have tube damage the first step of assessment would be an ultrasound. If the fallopian tubes show on the test it is highly probable that there is a problem as they are otherwise invisible.Endometriosis Problems
Possible Signs and Symptoms of Endometriosis
In cases in which a woman feels severe pain during ovulation there is a strong possibility she is suffering from some sort of gynecological problems, sometimes including endometriosis. Discomfort during ovulation can be manifested through pain in the lower abdomen, which starts about 2 weeks before the menstrual period. Depending on which ovary is active the pain can be felt either on the right or the left side. The pain can also vary from mild to severe and it can last for a few days.Causes of Pain in Ovaries and Fallopian Tubes
Most women do not feel any pain or discomfort during ovulation but those who do might be suffering from an underlying medical condition that needs to be diagnosed and treated. For instance, an inflammation of the fallopian tubes due to an infection called salpingitis can often cause painful ovulation and if left untreated lead to infertility. Also, chronic pelvic inflammation disease which occurs after an infection but in the pelvic area is a known contributor to ovulation pain. Various types of ovarian cysts can lead to pain, especially if they are bigger than normal. Ovarian and abdominal pain can also be caused by a pregnancy which takes place outside the womb, and if not treated promptly can have deadly consequences. Another very dangerous condition that produces abdominal pain is the inflammation of the appendix. It is recommended that individuals who have painful menstrual periods consult with their doctors to make sure there are no serious underlying conditions causing the discomfort. If the pain persists but no formal diagnosis is given there are some simple things that can be done in order to ease the discomfort. Resting in bed when the pain is intense and not engaging in any tiring activities often eases the pain. There are a number of menstrual pain killers available and most are fairly effective in treating the symptoms. Warmth applied to the pelvic area relaxes the tense muscles and reduces the pain. Also, birth control pills reduce the amount of vaginal bleeding and pain during the menstrual cycle, and they are often prescribed to ease the symptoms of heavy periods. However, they should not be used by women who are smoking or who are over 35 years old. In general, any kind of medical or pharmaceutical help that can be used for treating the signs of a possible disease should not be taken without consulting with a primary health care provider first.











Your thoughts on this
Loading...