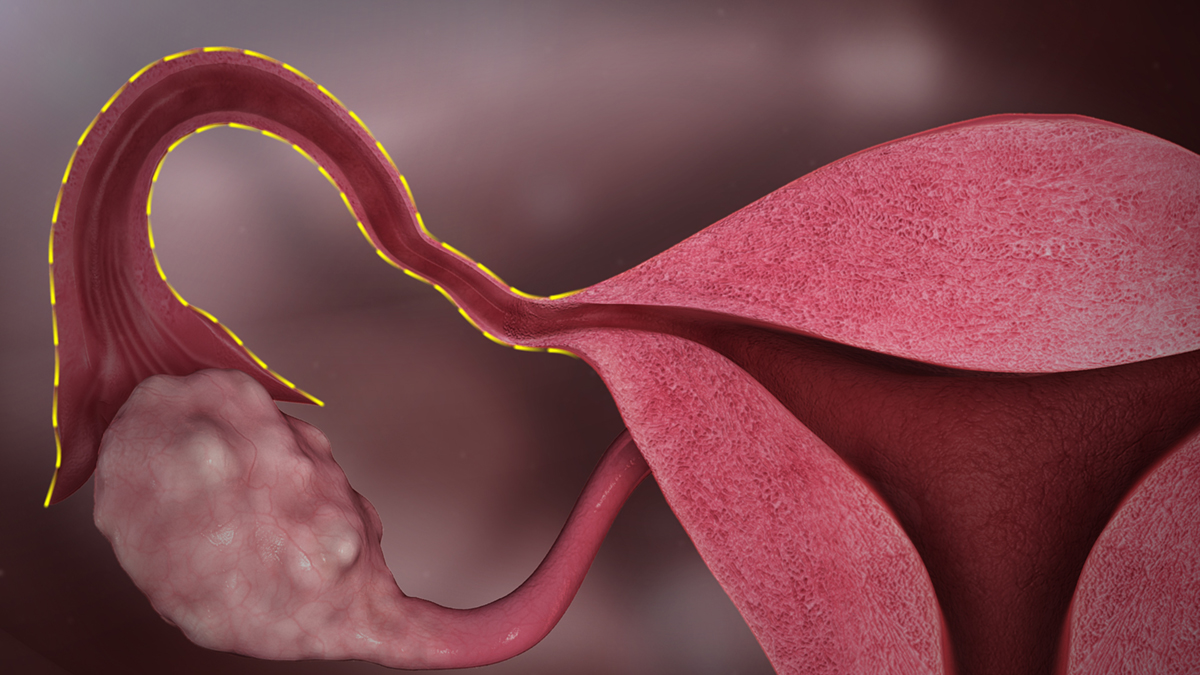
The fallopian tubes are pair of thin tubes, located on the both sides of the uterus, which play a vital role in ovulation and conception. The fallopian tubes lead egg that is broken out of its follicle released from the ovaries to the uterus. When the fallopian tubes become narrow or blocked, they prevent the mature egg from traveling to the uterus, which makes conception impossible. Tubal blockage can occur in one or both fallopian tubes. Fallopian tube blockage is the cause of infertility in 40% of infertile females and it is called tubal factor infertility.
Fallopian Tubes and InfertilityEvery month, during ovulation, ovaries release one mature egg, which travels to the uterus via fallopian tubes. In order for women to conceive, sperm must travel from the cervix though the uterus and into the tubes to reach the egg and fertilize it. Then sperm and the egg become an embryo that has to reach the uterus to be implanted. However, when one or both fallopian tubes are blocked the egg cannot be fertilized nor conception can take place. A woman may get pregnant in case that one tube is blocked and if ovaries function properly.
The fallopian tubes can be blocked totally or partially. Partially blocked fallopian tubes may cause a tubal pregnancy or ectopic pregnancy in which case a fetus cannot survive.
Hydrosalpinx is a specific kind of blocked fallopian tube that occurs when the tube dilates and fills with fluid. When the tube is blocked, this fluid can accumulate inside causing it to stretch and increase in size. This fluid blocks the sperm and egg thus preventing fertilization and conception.
Symptoms of Blocked Fallopian Tubes
Blocked fallopian tubes may not be identified because they rarely cause any symptom. Some women that have hydrosalpinx may experience lower abdominal pain and abnormal vaginal discharge. If blocked fallopian tubes are caused by endometriosis or pelvic inflammatory disease, menstrual period and sexual intercourse may be painful.
Causes for Blocked Fallopian Tubes
The fallopian tubes are most commonly blocked due to pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) that may occur as a result of a sexually transmitted disease. Even when a woman recovers from PID, she has increased risk of blocked fallopian tubes. Blocked tubes may occur, if a woman suffers from or has a history of Chlamydia or Gonorrhea. Endometriosis may be the cause of blocked tubes as well as tubal ligation procedures. Other causes include history of uterine infection caused by previous abortion or miscarriage, history of ruptured appendix, history of abdominal surgery and previous ectopic pregnancy.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Blocked tubes are mainly diagnosed with the help of hysterosalpingogram, a specialized x-ray. Other tests may include ultrasound, exploratory laparoscopic surgery and hysteroscopy. Treatment involves fertility medications if only one tube is blocked. Laparoscopic surgery may be used to unblock the tubes but it is not always successful.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...