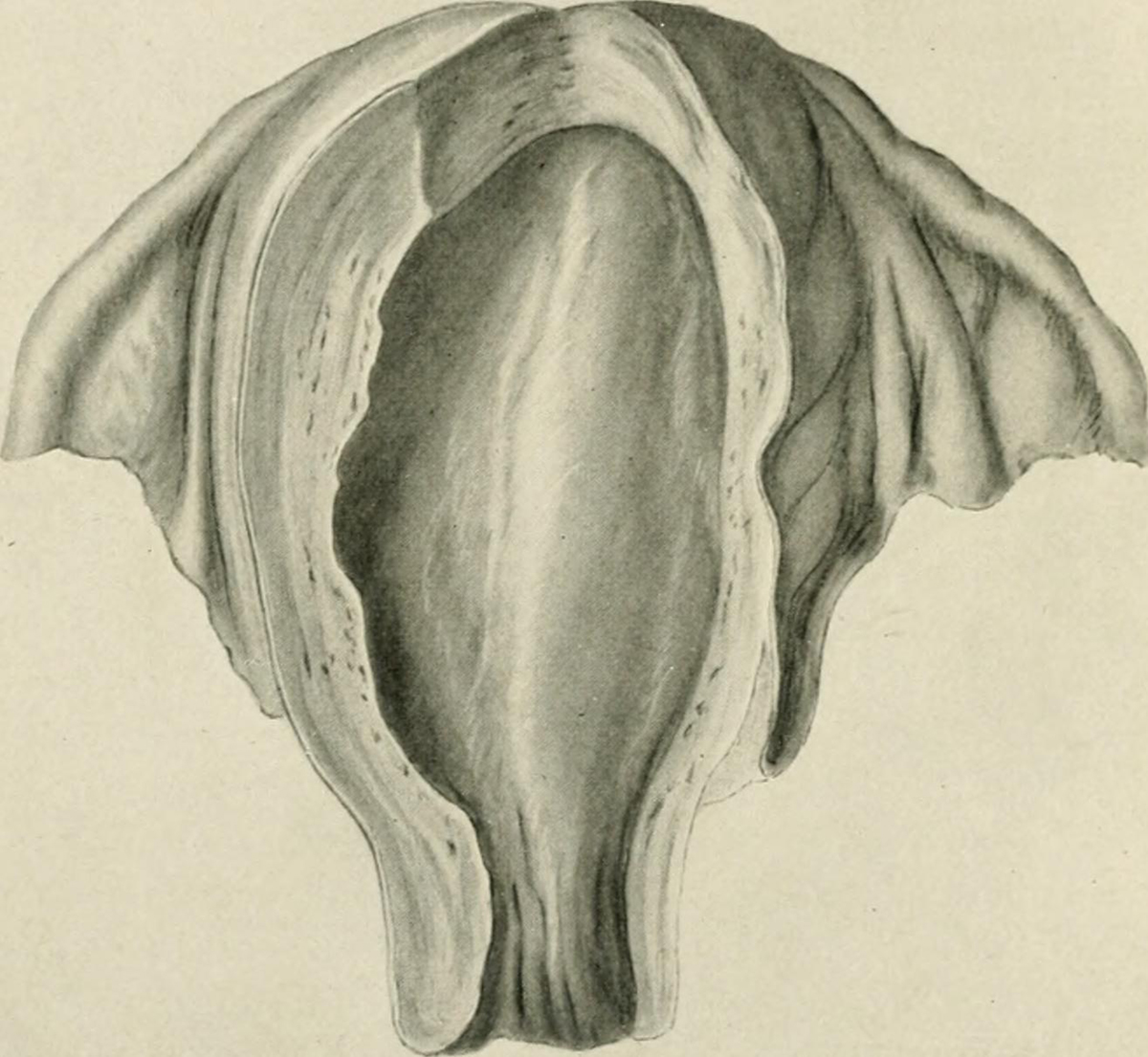
Fallopian tube infection is an infection of these female organs caused by bacteria. Women normally have two fallopian tubes and they are located in the pelvis. These organs connect the uterus with the ovaries allowing the egg released from the ovaries to be inseminated inside the very tubes and then sent to the uterus where it is implanted. The fallopian tubes are lined with a specific epithelium that contains ciliated cells. These cells are highly effective and assist in transfer of the ovum (the egg).
As in the case of many other organs even fallopian tubes can be affected by infection. Infection of fallopian tubes is medically known as salpingitis. Salpingitis can be acute and chronic. In acute form of the disease the fallopian tubes are inflamed, swollen and filled with excess of fluid. In severe form of salpingitis and if the infection is left untreated the fallopian tubes may be even filled with pus. If left untreated acute salpingitis may cause rupture of the affected fallopian tube and spread of the pus and infection to the surrounding tissues. This spread eventually leads to peritonitis, a serious inflammation of the peritoneum. Chronic form of the disease features with milder symptoms and signs but it carries great risk of damage to the fallopian tubes. Namely, prolonged inflammation leads to scaring and the affected tube may eventually become narrow not allowing the egg to be fertilized and transferred to the uterus. This is why chronic salpingitis commonly leads to infertility.
Causes of Fallopian Tube Infection
The infection can spread to the fallopian tubes from the vagina directly or via the lymphatic vessels. If the infection spreads via lymphatic vessels the chance that both fallopian tubes will be affected is greater. The most common infective agents that cause salpingitis include Streptococcus, Mycoplasma and Staphylococcus. Apart from the previously mentioned salpingitis may be a consequence of sexually transmitted diseases (gonorrhea, chlamydia etc.).
Symptoms of Fallopian Tube Infection
In some women salpingitis is asymptomatic. On the other hand, if there are symptoms of fallopian tube infection they include discomfort and/ or pain during sexual intercourse, discharge from the vagina, spotting between periods, pain during menstrual bleeding, severe abdominal pain on one or both sides of the lower abdomen and pain during ovulation. If the infection is severe a woman may complain about nausea, vomiting, fever and severe headache, general bodily weakness and frequent urination.
Treatment for Fallopian Tube Infection
After setting the diagnose patients suffering from fallopian tube infection are always administered antibiotics. In severe cases and if there are complications of the infection (such as rupture of the fallopian tube and subsequent peritonitis) patients undergo surgery. It is essential to treat fallopian tube infection and not allow it to become chronic. Chronic infection with no obvious signs and symptoms eventually leads to scaring of the affected fallopian tube and problems with conceiving.









Your thoughts on this
Loading...