When is Vascular Surgery Necessary?
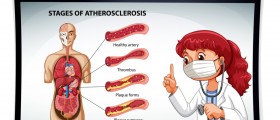
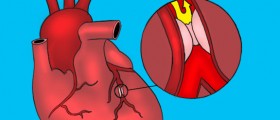
Diseases of vascular system such as arteriosclerosis, blood clots and other arterial and venous diseases, as well as diseases of lymphatic system are treated by vascular surgery very frequently. The majority of these conditions is a result of either clogged or weakened blood vessels, or the damage of heart valves, and many people suffer from such problems.

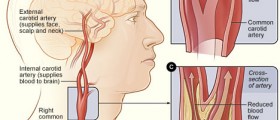
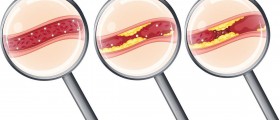
With age, the chances that even those who are perfectly healthy will develop some kind of that problem increase, too. However, since this is an invasive method of treatment, first it is necessary to try out other methods that are less invasive and do not require surgery procedures. There are several vascular surgery procedures, and among them are: traditional open surgery for aneurysms, most commonly used in cases of abdominal aortic aneurysms; endovascular grafting for aneurysms, with which aortic aneurysm is treated; bypass for atherosclerosis, which helps in cases of narrowed or blocked arteries; carotid endarterectomy, during which the plaque from the inside of carotid artery is removed; atherosclerosis atherectomy, during which the plaque from the affected blood vessel is being removed with the help of a sharp catheter; and atherosclerosis endarterectomy, which is an open surgery, during which plaque from the blood vessel is removed surgically.
Which procedure will be suggested to the patient depends on the disease and the part of the body in which the problem is.
What Are the Complications of Vascular Surgery?
Whenever some kind of a procedure involves incisions and cuts, there have to be some risks involved, no matter how much the doctors may try to do everything in their power to reduce or eliminate them. As for vascular surgery procedures, the ones that are done on major blood vessels are a bit more likely to cause complications. Besides that, there are certain groups of patients who are at higher risk of developing some kind of a complication, and these groups include people who smoke, people who are over 65 years, and people who have some other disease.
The most common complications are bleeding and swelling in leg, but they are rather minor, in comparison to the possible major complications such as heart attack, stroke, damage of the circulatory system, blocked or failed grafts, and impotence. Many of them are life-threatening and may even cause the death of the patient, which is why it is necessary to inform the patient in advance about every possible outcome.
- Pneumonia had the largest impact on the incidence of end-organ dysfunction in carotid endarterectomy patients (adjusted population-attributable fraction, 24.4%; 95% confidence interval, 20.6-28.1), and cerebrovascular accident had the largest impact on mortality in these patients (adjusted PAF, 23.1%; 95% confidence interval, 18.5-27.3).
- In patients undergoing abdominal or lower extremity vascular surgery, bleeding and pneumonia had the largest impact on clinical outcomes and need for prolonged hospitalization, and surgical site infection had the largest impact on hospital readmission.
- In contrast, prevention of venous thromboembolism, urinary tract infection, and myocardial infarction do not demonstrate substantial impact on patient outcomes or resource utilization in either group of vascular surgery patients.
- The most common index complications in patients undergoing carotid endarterectomy were bleeding (2.2%) and stroke (1.7%). The most common index complications in patients undergoing an abdominal/lower extremity vascular operation were bleeding (30.4%) and surgical site infection (7.1%).









Your thoughts on this
Loading...